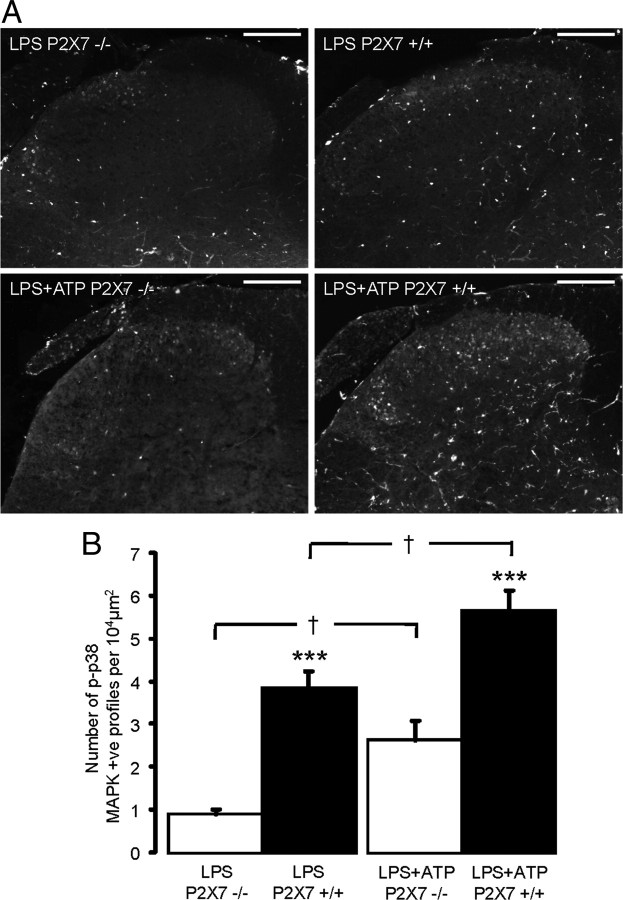
Figure 5.
Disruption of P2X7 receptor signaling attenuates both LPS- and ATP-induced p-p38 MAPK phosphorylation in mouse dorsal horn slices. A, LPS superfusion results in an increase in p38 MAPK phosphorylation in SC slices from wild-type mice, which is absent in SC slices from P2X7 knock-out mice. Similarly, following LPS priming, ATP superfusion results in an increase in p38 MAPK phosphorylation in SC slices from wild-type mice, which is attenuated in P2X7 receptor knock-out mice. Scale bars, 100 μm. B, Quantification of p-p38 immunoreactivity in mouse SC slices (n = 5–6 slices per group). ***p < 0.001 knock-out versus wild-type, †p < 0.05 compared to indicated group, one-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey's test.