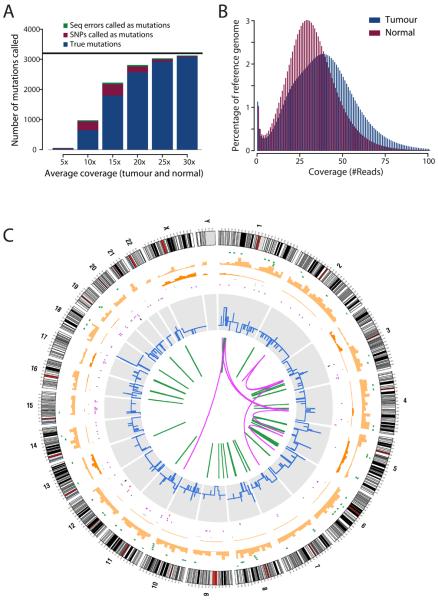
Figure 1.
The compendium of somatic mutations in a small cell lung cancer genome. (A) Power calculations showing the number of true somatic substitutions detected (blue) and mis-calls (SNPs called as somatic mutations, burgundy, and sequencing errors called as mutations, green) for different levels of sequence coverage. Calculations are based on a true mutation prevalence of 1/Mb (black line). (B) Histogram of the actual coverage achieved per base of the tumour (blue) and normal (burgundy) genomes. (C) Figurative representation of the catalogue of somatic mutations in the genome of NCI-H209. Chromosome ideograms are shown around the outer ring and are oriented pter-qter in a clockwise direction with centromeres indicated in red. Other tracks contain somatic alterations: validated insertions (light green rectangles); validated deletions (dark green rectangles); heterozygous (light orange bars) and homozygous (dark orange bars) substitutions shown by density per 10 megabases; coding substitutions (coloured squares; silent in grey, missense in purple, nonsense in red and splice site in black); copy number (blue lines); validated intrachromosomal rearrangements (green lines); validated interchromosomal rearrangements (purple lines).