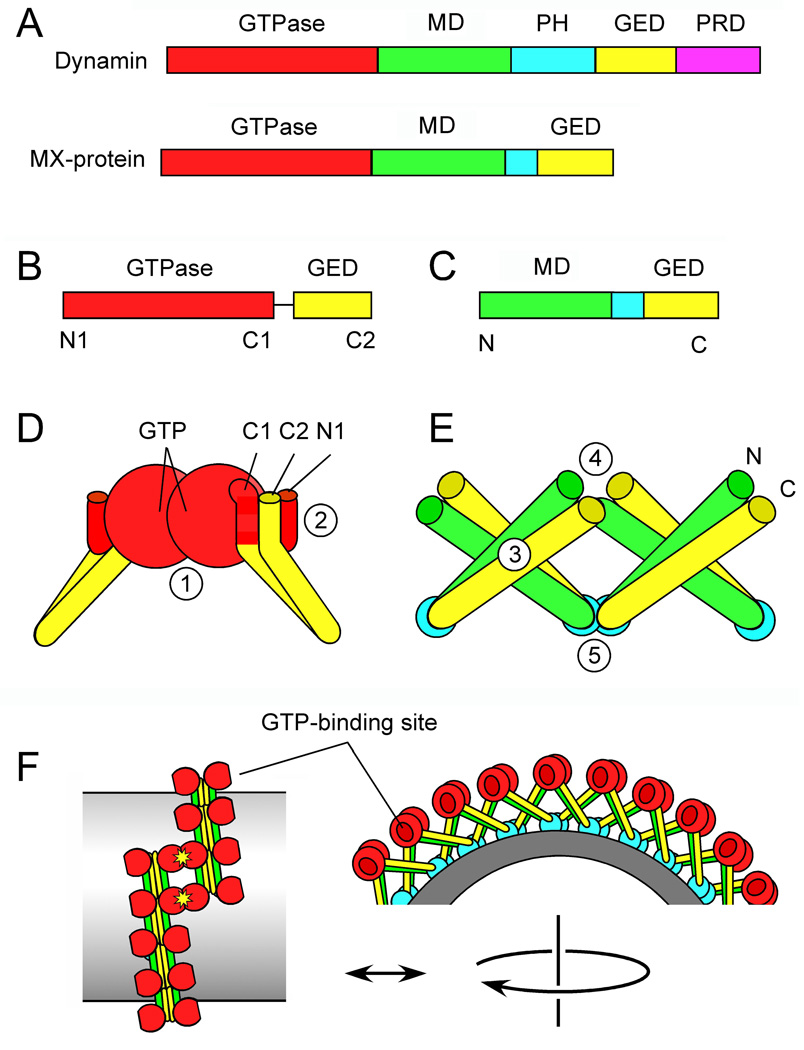
Figure 1. Dynamin protein domains and the newly solved structures.
(A) Protein domains in Dynamin and MxA. (B) Dynamin GTPase-GED fusion protein crystallized by Chappie et al. (2010). Amino and carboxy terminal α-helices are indicated by N1, C1 and C2. (C) MxA fragment crystallized by Gao et al. (2010). (D) Key features of the GTPase-GED structure, showing dimerization of two GTPase domains. The interface with GTP-binding sites (1) is buried in this drawing. The BSE is formed by interactions between N1, C1 and C2 helices (2). (E) Key features of the MD-GED structure, showing interactions with adjacent subunits at three different points (3–5) (F) Hypothetical arrangement of dynamin subunits in a spiral suggested by the newly identified interactions and by cryoEM.