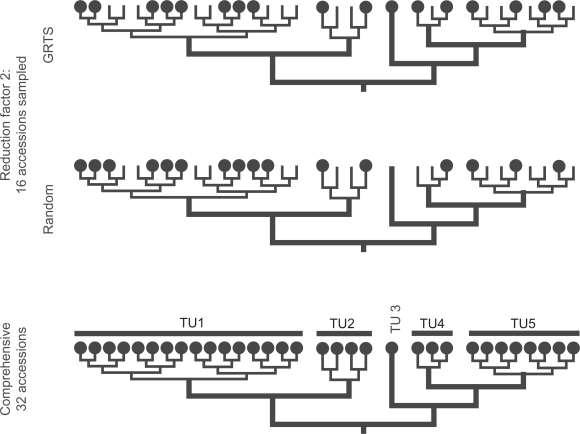
Figure 1.
Scheme illustrating the GRTS procedure (this study) in comparison to random taxon jackknifing.47 In contrast to random jackknifing, GRTS assures that each replicate includes always members of all pre-defined TU (in the given example TU 3 is missing in the random jackknife replicate) and that each TU is sampled proportionally to its original size. For instance, TU 1 includes 16 accessions. Thus, using a reduction factor of 2 each GRTS replicate will include exactly 8 members of TU 1. The number in random jackknife replicates may vary, resulting in an over- (TU 1 in given example) or underrepresentation of TUs (TUs 4 and 5).