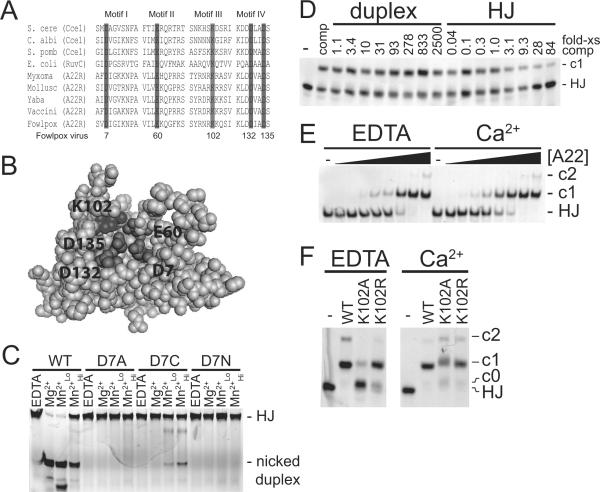
Figure 1.
DNA binding and cleavage by FPV resolvase and active site mutants. A) Protein sequence alignment of four conserved motifs of various RNase H-like family Holliday junction resolvases (adapted from Lilley and White12). Shading indicates residues that are 100% conserved within the RNase H-like resolvases. Amino acid numbering refers to fowlpox virus. S. cere, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; C. albi, Candida albicans; S. pomb, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; E. coli, Escherichia coli; Myxoma, myxoma virus; Mollusc, molluscum contagiosum virus; Yaba, Yaba monkey tumor virus; Vaccini, vaccinia virus; Fowlpox, fowlpox virus. B) Model of fowlpox resolvase tertiary structure showing the inferred active site, constructed with SWISS-MODEL37 using the RuvC crystal structure as a template. C) Native PAGE analysis of a representative metal rescue experiments. DNA cleavage reactions for the indicated amino acid substituted proteins were carried out in the various metal conditions indicated above the gel. EDTA, 1 mM EDTA; Mg2+, 15 mM MgCl2; Mn2+Lo, 0.5 mM MnCl2; Mn2+Hi, 5 mM MnCl2. Reaction products are labeled to the right of the gel. HJ, Holliday junction substrate. D) Native PAGE analysis of DNA binding by wild type protein in the presence of duplex or Holliday junction competitor DNA. DNA binding reactions were performed with 48 ng of wild type protein (2.4 pmol, 120 nM) and 2 nM Holliday junction probe DNA in the presence of 1 mM EDTA. Numbers above the gel lanes indicate the fold-excess of competitor DNA to probe DNA (wt/ wt). E) Binding of wild-type FPV resolvase to DNA in the presence of EDTA or Ca2+. DNA binding reactions were performed with various amounts of wild type protein and 2 nM Holliday junction DNA in the presence of either 1 mM EDTA (EDTA) or 1 mM CaCl2 (Ca2+). -, no protein; solid triangle indicate increasing amounts of protein from left to right: 0.3, 0.9, 2.6, 7.9, 24, 71, 213, 640 ng (the 640 ng amount corresponds to 1.6 μM). Resolvase-DNA complexes are labeled to the right of the gel. F) Effect of Ca2+ on DNA binding by amino acid substituted resolvases. DNA binding reactions were performed with 600 ng of the indicated protein (1.5 μM) and 2 nM of the Holliday junction probe DNA in the presence of either 1 mM EDTA (EDTA) or 1 mM CaCl2 (Ca2+).