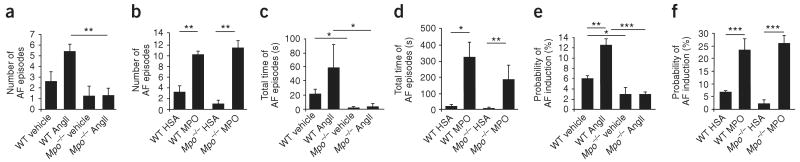
Figure 2.
Analysis of atrial fibrillation inducibility in Mpo−/− and WT mice in vivo. (a–d) After pretreatment with AngII or saline (vehicle) for 14 d (n = 10–16 per group) (a,c) or MPO or human serum albumin (HSA) for 7 d (n = 6–9 per group) (b,d), WT and Mpo−/− mice underwent electrophysiological investigation. (a,b) Quantification of the number of atrial fibrillation (AF) episodes. **P < 0.01. (c,d) Total time of atrial fibrillation episodes. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (e,f) Probability of induction of atrial fibrillation, defined as inducible episodes divided by number of total testing maneuvers applied. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. All data are means ± s.d. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test.