Abstract
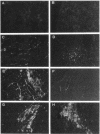
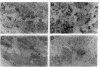
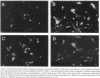
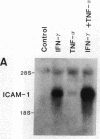
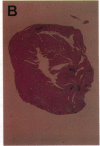
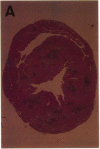
A cell-mediated autoimmune mechanism has been strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of viral myocarditis. Using a murine model of myocarditis caused by coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3), we previously reported that the heart is infiltrated first by natural killer cells, which express a cytolytic factor, perforin, and then by activated T cells. This action may play an important role in the pathogenesis of the observed myocardial cell damage. Cell-cell contact and adhesion is required in immune responses, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), which is a ligand for lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1), plays an important role in this process. To investigate the essential role of the ICAM-1/LFA-1 pathway in the cell-mediated cytotoxicity involved in viral myocarditis, we examined by immunofluorescence the expression of ICAM-1 in murine hearts with acute myocarditis caused by CVB3. We also evaluated the induction of ICAM-1 in cultured cardiac myocytes treated with cytokines by immunofluorescence and Northern blot hybridization. Furthermore, we analyzed the effects of in vivo administration of anti-ICAM-1 mAbs on the inflammation associated with acute viral myocarditis. We found that CVB3-induced murine acute myocarditis resulted in enhanced expression of ICAM-1 in myocardial cells. The expression of ICAM-1 in myocardial cells could be induced in vitro by IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, which were shown to be synthesized by the infiltrating cells. In vivo treatment with F(ab')2 fragments of an anti-ICAM-1 mAb significantly reduced the myocardial inflammation induced by CVB3. These data strongly suggest that the expression of ICAM-1 in myocardial cells plays a critical role in the cell-mediated cytotoxicity involved in acute viral myocarditis.
Full text
PDF


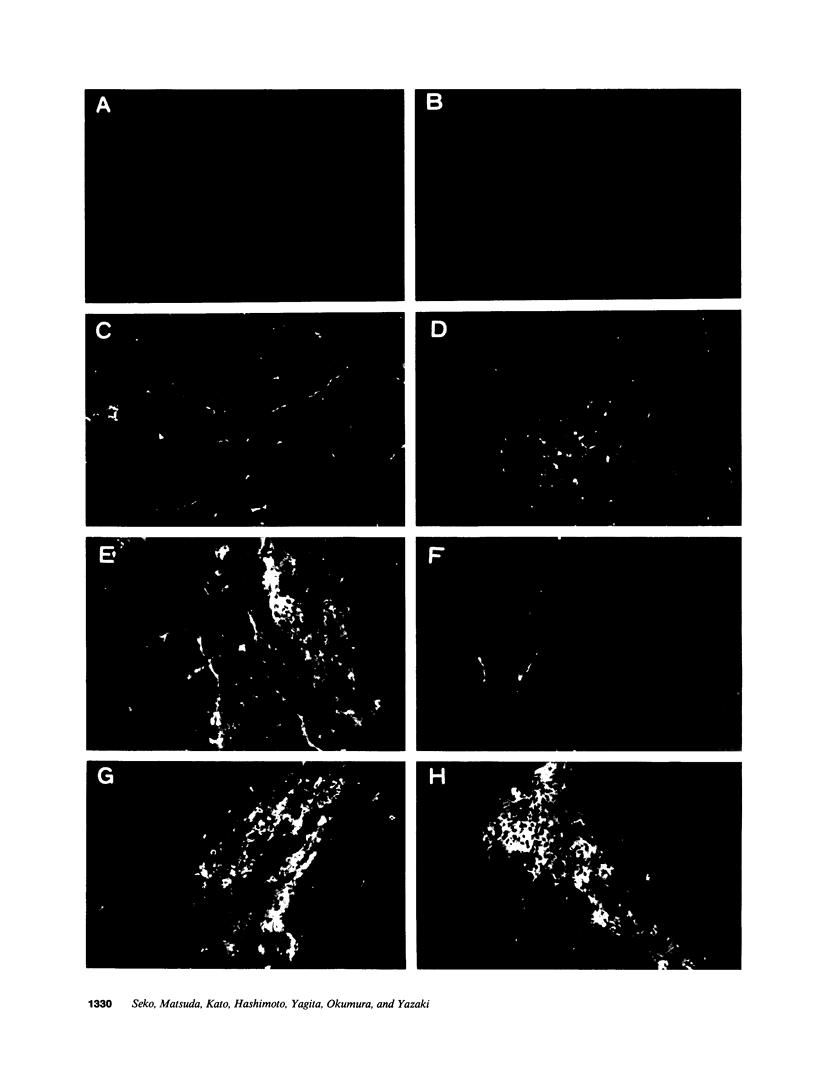
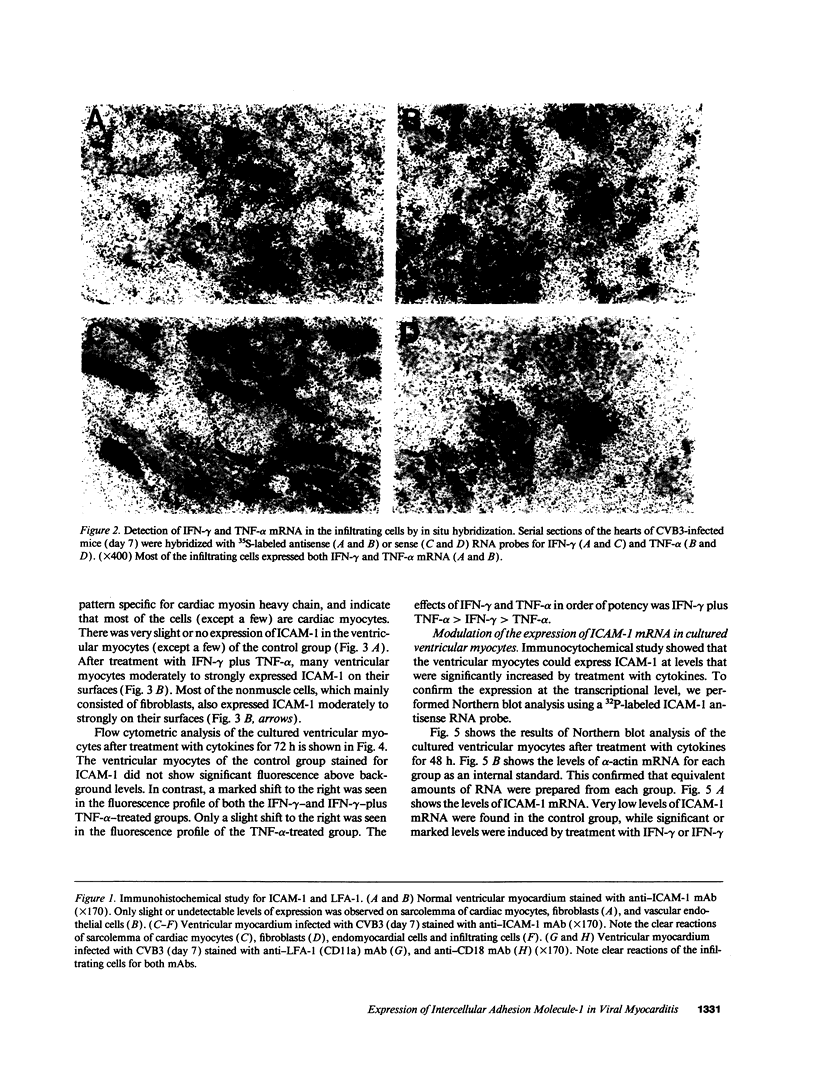
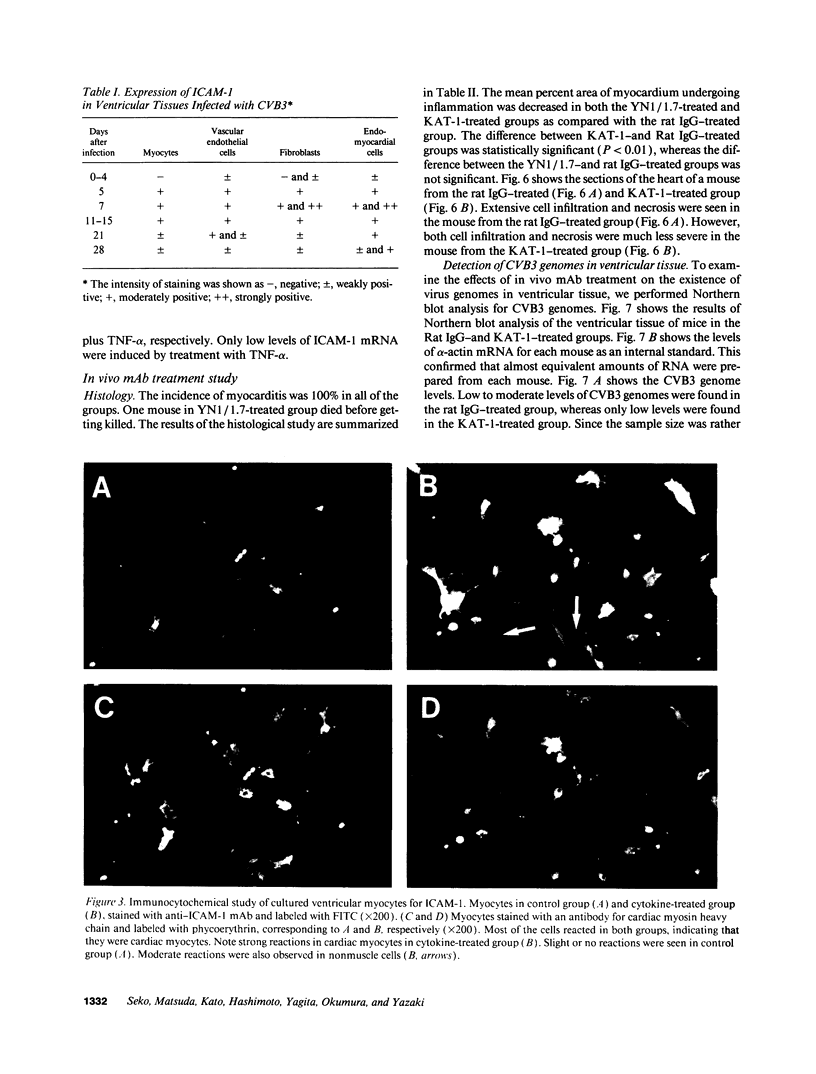
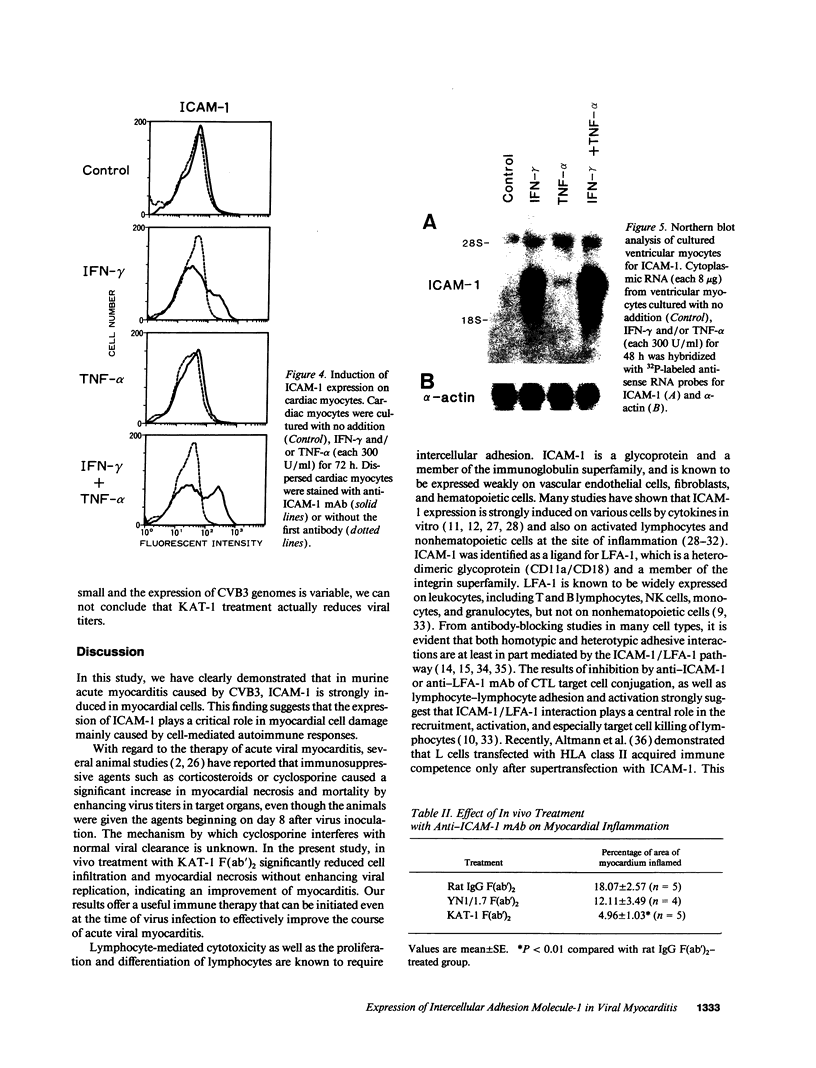



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann D. M., Hogg N., Trowsdale J., Wilkinson D. Cotransfection of ICAM-1 and HLA-DR reconstitutes human antigen-presenting cell function in mouse L cells. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):512–514. doi: 10.1038/338512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Wawryk S. O., Burns G. F., Fecondo J. V. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) has a central role in cell-cell contact-mediated immune mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3095–3099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Cutri A., Wilkinson D., Boyd A. W., Harrison L. C. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 is induced on isolated endocrine islet cells by cytokines but not by reovirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4282–4286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavender D., Saegusa Y., Ziff M. Stimulation of endothelial cell binding of lymphocytes by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1855–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Singer K. H., Tuck D. T., Springer T. A. Adhesion of T lymphoblasts to epidermal keratinocytes is regulated by interferon gamma and is mediated by intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1323–1340. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression of murine immune interferon cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths C. E., Nickoloff B. J. Keratinocyte intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression precedes dermal T lymphocytic infiltration in allergic contact dermatitis (Rhus dermatitis). Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1045–1053. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths C. E., Voorhees J. J., Nickoloff B. J. Characterization of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and HLA-DR expression in normal and inflamed skin: modulation by recombinant gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 Apr;20(4):617–629. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G. M., Mueller C. Expression of perforin and granzymes in vivo: potential diagnostic markers for activated cytotoxic cells. Immunol Today. 1991 Nov;12(11):415–419. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90145-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie M., Lodge P. A., Huber S. A. Cardiac injury in myocarditis induced by Coxsackievirus group B, type 3 in Balb/c mice is mediated by Lyt 2 + cytolytic lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 15;88(2):558–567. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale L. P., Martin M. E., McCollum D. E., Nunley J. A., Springer T. A., Singer K. H., Haynes B. F. Immunohistologic analysis of the distribution of cell adhesion molecules within the inflammatory synovial microenvironment. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jan;32(1):22–30. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horley K. J., Carpenito C., Baker B., Takei F. Molecular cloning of murine intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1). EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2889–2896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. P., Stade B. G., Holzmann B., Schwäble W., Riethmüller G. De novo expression of intercellular-adhesion molecule 1 in melanoma correlates with increased risk of metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):641–644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolf R., Hofschneider P. H. Molecular cloning of the genome of a cardiotropic Coxsackie B3 virus: full-length reverse-transcribed recombinant cDNA generates infectious virus in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4818–4822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krensky A. M., Robbins E., Springer T. A., Burakoff S. J. LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3 antigens are involved in CTL-target conjugation. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2180–2182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krensky A. M., Sanchez-Madrid F., Robbins E., Nagy J. A., Springer T. A., Burakoff S. J. The functional significance, distribution, and structure of LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3: cell surface antigens associated with CTL-target interactions. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. Purified intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1). Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Caravatti M., Robert B., Cohen A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Gros F., Buckingham M. E. Mouse actin messenger RNAs. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid molecule containing a complementary DNA transcript of mouse alpha-actin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Kikuchi N., Ohara O., Teraoka H., Yoshida N., Kawade Y. Purification and characterization of recombinant murine immune interferon. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 15;205(2):200–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80897-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura T., Itoh T. Higher level expression of lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) on in vivo natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):2077–2080. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell J. B., Reap E. A., Robinson J. A. The effects of cyclosporine on acute murine Coxsackie B3 myocarditis. Circulation. 1986 Feb;73(2):353–359. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Vassallo C., Luhowskyj S., Chi-Rosso G., Lobb R. Direct expression cloning of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, a cytokine-induced endothelial protein that binds to lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1203–1211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90775-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Hayflick J. S., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the cDNA for murine tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6060–6064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto J., Takei F., Gendelman R., Christenson B., Biberfeld P., Patarroyo M. MALA-2, mouse homologue of human adhesion molecule ICAM-1 (CD54). Eur J Immunol. 1989 Sep;19(9):1551–1557. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Czajkowski M., O'Neill M. M., Marlin S. D., Mainolfi E., Merluzzi V. J. Induction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on primary and continuous cell lines by pro-inflammatory cytokines. Regulation by pharmacologic agents and neutralizing antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Simon P., Thompson S., Springer T. A. Mapping of antigenic and functional epitopes on the alpha- and beta-subunits of two related mouse glycoproteins involved in cell interactions, LFA-1 and Mac-1. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):586–602. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seko Y., Shinkai Y., Kawasaki A., Yagita H., Okumura K., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Expression of perforin in infiltrating cells in murine hearts with acute myocarditis caused by coxsackievirus B3. Circulation. 1991 Aug;84(2):788–795. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.2.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seko Y., Tsuchimochi H., Nakamura T., Okumura K., Naito S., Imataka K., Fujii J., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Expression of major histocompatibility complex class I antigen in murine ventricular myocytes infected with Coxsackievirus B3. Circ Res. 1990 Aug;67(2):360–367. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.2.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer K. H., Tuck D. T., Sampson H. A., Hall R. P. Epidermal keratinocytes express the adhesion molecule intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in inflammatory dermatoses. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 May;92(5):746–750. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12722441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei F. Inhibition of mixed lymphocyte response by a rat monoclonal antibody to a novel murine lymphocyte activation antigen (MALA-2). J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1403–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogetseder W., Feichtinger H., Schulz T. F., Schwaeble W., Tabaczewski P., Mitterer M., Böck G., Marth C., Dapunt O., Mikuz G. Expression of 7F7-antigen, a human adhesion molecule identical to intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in human carcinomas and their stromal fibroblasts. Int J Cancer. 1989 May 15;43(5):768–773. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawryk S. O., Novotny J. R., Wicks I. P., Wilkinson D., Maher D., Salvaris E., Welch K., Fecondo J., Boyd A. W. The role of the LFA-1/ICAM-1 interaction in human leukocyte homing and adhesion. Immunol Rev. 1989 Apr;108:135–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Cohen S., Makgoba M. W., Borysiewicz L. K. Expression of an intercellular adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, by human thyroid cells. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;122(1):185–191. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F. Viral myocarditis. A review. Am J Pathol. 1980 Nov;101(2):425–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F., Woodruff J. J. Involvement of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of coxsackie virus B3 heart disease. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1726–1734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazaki Y., Tsuchimochi H., Kuro-o M., Kurabayashi M., Isobe M., Ueda S., Nagai R., Takaku F. Distribution of myosin isozymes in human atrial and ventricular myocardium: comparison in normal and overloaded heart. Eur Heart J. 1984 Dec;5 (Suppl F):103–110. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/5.suppl_f.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. H., Klavinskis L. S., Oldstone M. B., Young J. D. In vivo expression of perforin by CD8+ lymphocytes during an acute viral infection. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2159–2171. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. H., Peterson L. B., Wicker L. S., Persechini P. M., Young J. D. In vivo expression of perforin by CD8+ lymphocytes in autoimmune disease. Studies on spontaneous and adoptively transferred diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3994–3999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]