TABLE 3.
Statistical models describing mutational fitness effects for 77 viable, nonbeneficial, mutations
| Model | Probability density functiona | Parameter estimatesb | Log-likelihoodc | Goodness of fitd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exponential | 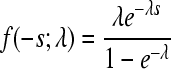 |
λ = 8.144 (6.867;9.564) | 35.11 | 0.957 |
| Gamma | 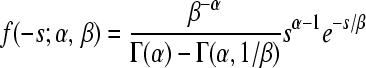 |
α = 0.344 (0.276;0.425) | 58.80 | 0.993 |
| β = 0.387 (0.262;0.676) | ||||
| Beta | 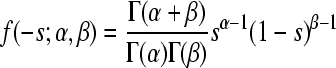 |
α = 0.315 (0.257;0.385) | 58.35 | 0.992 |
| β = 2.265 (1.661;3.017) | ||||
| Log-normal |  |
μ = −2.895 (−3.848;−0.916) | 60.97 | 0.994 |
| σ = 3.473 (2.550;4.691) | ||||
| Weibull | 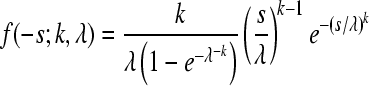 |
λ = 0.079 (0.049;0.161) | 60.32 | 0.994 |
| k = 0.440 (0.358;0.530) |
The constraint 0 ≤ −s ≤ 1 was imposed (0 < −s ≤ 1 for the Log-normal) and probability density functions were normalized accordingly.
Obtained by maximum likelihood, accounting for experimental error; confidence intervals correspond to an increase of one log-likelihood unit.
Calculated from probability densities. Since the latter can be larger than 1, the log-likelihood can be positive.
Squared correlation coefficient (r2) between the observed and predicted cumulative distribution functions.
