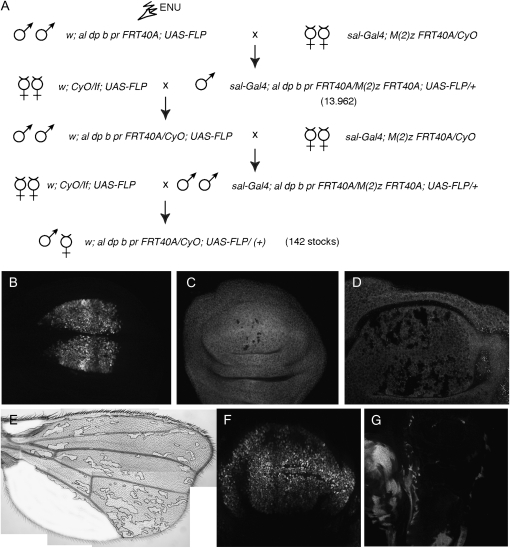
Figure 1.—
Crosses and Gal4 lines used to generate homozygous mutant wings in heterozygous flies. (A) Chromosomes and genetic crosses used to generate mosaic flies. Males of w; al dp b pr FRT40A; UAS-FLP genotype were treated with ENU and crossed in groups of 50 with salEPv-Gal4; M(2)Z FRT40A/CyO females (first row). The sal-Gal4; M(2)Z FRT40A/al dp b pr FRT40A; UAS-FLP/+ male progeny (13,962 males, second row) was screened for wing phenotypes. Selected males were crossed with w; CyO/If; UAS-FLP females, and the male progeny of w; al dp b pr FRT40A/CyO; UAS-FLP genotype were crossed with salEPv-Gal4; M(2)Z FRT40A/CyO females. We established stable w; al dp b pr FRT40A;UAS-FLP/+ stocks when the original phenotype was found in the progeny of this last cross (142 cases). (B) Expression of GFP in the wing blade region of the salEPv-Gal4/UAS-GFP wing disc. (C and D) Early (C) and late (D) third instar wing discs of salEPv-Gal4; M(2)Z FRT40A tubGFP/al dp b pr FRT40A; UAS-FLP/+ genotype, showing the clones as black spots. (E) Adult wing of f36a salEPv-Gal4; M(2)Z FRT40A Pf+30C/al dp b pr FRT40A; UAS-FLP/+ genotype, showing the area not covered by forked clones in white. (F) Third instar wing disc showing the expression of the 638-Gal4 line (638-Gal4/UAS-GFP). (G) Third instar wing disc of 638-Gal4; M(2)Z FRT40A tubGFP/al dp b pr FRT40A; UAS-FLP/+ genotype. Most of the wing blade is composed of al dp b pr FRT40A homozygous cells (shown in black).