Figure 7.—
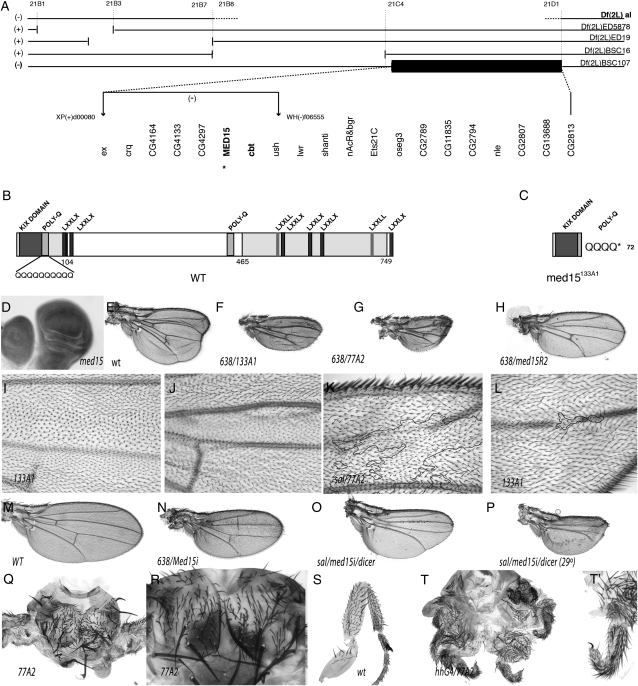
The complementation group formed by 77A2 and 133A1 corresponds to med15. (A) Chromosomal interval 21B3–21C4 and extent of the deficiencies used (named to the right) shown as open spaces between horizontal bars. The region included in Df(2L)BSC107, which defines the localization of the 77A2/133A1 complementation group, is shown as a solid bar, and the genes included in this deficiency are shown at the bottom. The position of two PiggyBac insertions used to generate the Df(2L)d0080-f06555 chromosome is shown by vertical arrows. (B) Protein sequence and domains of Med15. (C) Expected protein produced by the med15133A1 allele. (D) Generalized expression of med15 in the wing disc. (E) Control wing of 638-Gal4/+; FRT40A al dp b pr/FRT40A M(2)z; UAS-FLP/+ genotype showing the characteristic dp phenotype. (F and G) Homozygous wings for the med15 alleles med15133A1 (133A1) (E) and med1577A2 (77A2) (F). The genotypes of these wings are 638-Gal4/+; FRT40A al med15133A1 dp b pr/FRT40A M(2)z; UAS-FLP/+ (F) and 638-Gal4/+; FRT40A al med1577A2 dp b pr/FRT40A M(2)z; UAS-FLP/+ (G). (H) Phenotype of med15f04180 homozygous wing in 638-Gal4/+; FRT40A al med15f04180 dp b pr/FRT40A M(2)z; UAS-FLP/+ female flies (compare the wing size with its control shown in M). (I and J) Mitotic recombination clones generated in hsFLP1.22 f36a; ck P[f+]30C FRT40A/al med15133A1 dp b pr FRT40A flies. The clone in I is labeled with ck and is wild type for the med15 gene (twin spot). The clone in J is labeled with forked and is homozygous for the med15133A1 allele. Both clones are located in the L3/L4 intervein, occupying a large fraction of this dorsal (I) and ventral (J) intervein. (K) med1577A2 clone labeled with forked generated in f36a salEPv-Gal4/+; FRT40A al med1577A2 dp b pr/FRT40A P[f+]30C M(2)z; UAS-FLP/+ flies. The forked territory is enclosed by a solid line and is associated with the loss of the ventral L2 vein. (L) Small med15133A1 clone in the distal dorsal L4 vein causing the loss of this vein. (M–P) Phenotypes resulting from the expression of med15 interference RNA (med15i) in the genotypes 638-Gal4/+; UAS-med15i (N), salEPv-Gal4/UAS-med15i; UAS-dicer/+ (O), and salEPv-Gal4/UAS-med15i; UAS-dicer/+ grown at 29° (P). The wild-type control wing is shown in M. (Q and R) Two examples of thoraxes taken at different magnification showing the failure in the fusion between the left and the right hemithorax when the central region is occupied by med1577A mutant cells (labeled with forked in hsFLP1.22 f36a; P[f+]30C M(2)z FRT40A/al med1577A2 dp b pr FRT40A flies). (S) Wild-type male first leg. (T and T′) Two examples of legs taken at different magnifications (T′ is ×4 T) showing the defects in leg morphogenesis and tarsal segmentation in w; M(2)z P[f+]30C FRT40A/al med1577A dp b pr FRT40A; hh-Gal4/UAS-FLP flies.