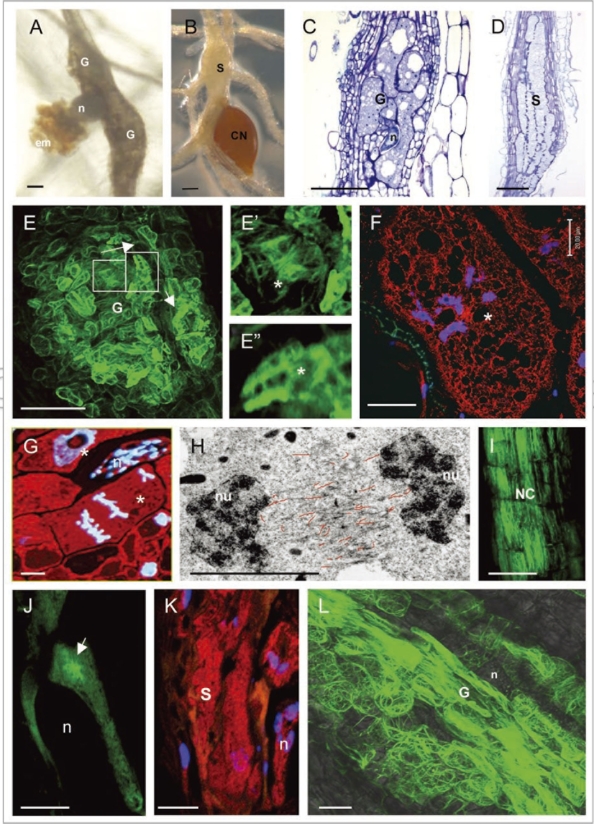
Figure 1.
(see opposite page)Feeding site morphology and actin cytoskeleton organization in feeding cells induced by RKN and CN. (A) Root-knots or galls induced by Meloidogyne incognita in A. thaliana; (B) a syncytium induced by Heterodera schachtii in A. thaliana; (C) longitudinal section of a gall stained with toluidine blue; (D) section of a syncytium stained with toluidine blue; (E) actin organisation in a gall (E-E″ and L show labeling with Fimbrin-GFP); (E′) actin bundles in the giant cell cortex; (E″) diffuse and filamentous actin fluorescence in a giant cell; (F) actin staining with anti-actin in a giant cell of a gall (actin in red and nuclei in blue); (G) anaphase giant cell showing no structured actin label (red) between the chromosomes (blue); (H) electron micrograph showing misalignment of F-actin (traced with red lines) in a phragmoplast of a giant cell; (I) longitudinal actin bundles in neighboring cells of a syncytium (I and J show labeling with Talin-GFP); (J) young syncytium with radial actin bundles focused towards the nematode head; (K) syncytium showing diffuse and fragmented microfilaments (red) and nuclei (blue), (L) accumulation of F-actin cables in the giant cells of ADF2 knockdown line. G, gall; n, nematode; em, egg mass; CN, cyst nematode; S, syncytium; *, giant cell; nu, nucleus; NC, neighboring cells. Bars (A–E) = 100 µm; (F, G and I–L) = 50 µm; (H) = 5 µm.