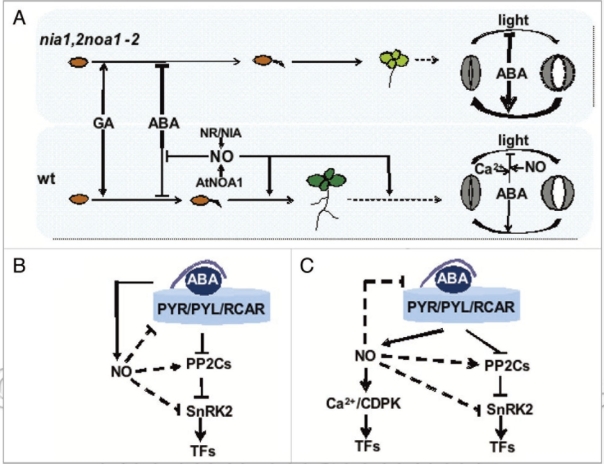
Figure 1.
Interactions between NO and ABA results in modulated sensitivity to ABA throughout development. (A) NO synthesized through nitrate reductase (NR/NIA) and NO associatedI (AtNOA1) protein regulate germinative and post-germinative development as well as stomata movements through modulation of the sensitivity to ABA. Arrows and bars represent positive and negative effects, and the thickness of lines are proportional to the magnitud of regulatory effects. (B) Scheme of a minimal ABA signalling module and the potential targets of NO. Dashed lines represent effects still to be demonstrated. (C) ABA signalling in stomata guard cells through Ca2+-dependent and -independent pathways and the potential interactions with NO as represented by dashed lines.