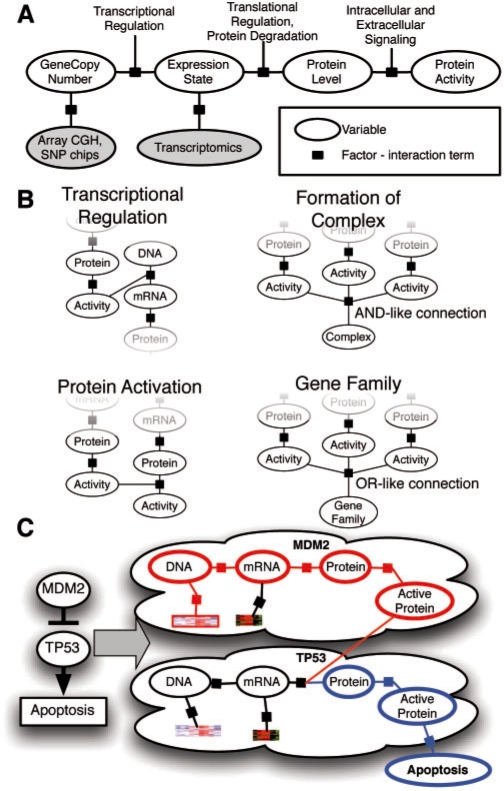
Fig. 3.
Conversion of a genetic pathway diagram into a PARADIGM model. A. Data on a single patient is integrated for a single gene using a set of four different biological entities for the gene describing the DNA copies, mRNA and protein levels, and activity of the protein. B. PARADIGM models various types of interactions across genes including transcription factors to targets (upper-left), subunits aggregating in a complex (upper-right), post-translational modification (lower-left) and sets of genes in a family performing redundant functions (lower-right). C. Toy example of a small sub-pathway involving P53, an inhibitor MDM2, and the high level process, apoptosis as represented in the model.