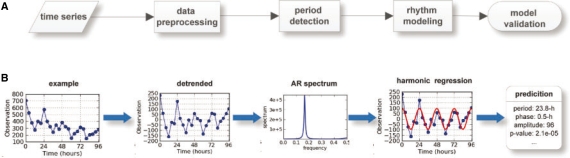
Fig. 1.
The diagram of our methodology (named ARSER) and a case study. (A) Analysis flowchart. First, data pre-processing by linear trend removal (detrending), then period detection by searching peaks from the AR spectrum. With the periods derived from the AR spectrum, harmonic regression is carried out to model circadian rhythms by fitting the detrended time-series with trigonometric functions. Finally, ARSER describes the periodicity by several parameters: period, phase, amplitude, statistical significance and so on. (B) An example of rhythmicity analysis by ARSER. The synthetic time-series is generated by the following equation: 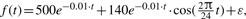 , where t∈[0, 96] with 4 h intervals and ε is white noise following (μ=0, σ=40) normal distribution.
, where t∈[0, 96] with 4 h intervals and ε is white noise following (μ=0, σ=40) normal distribution.