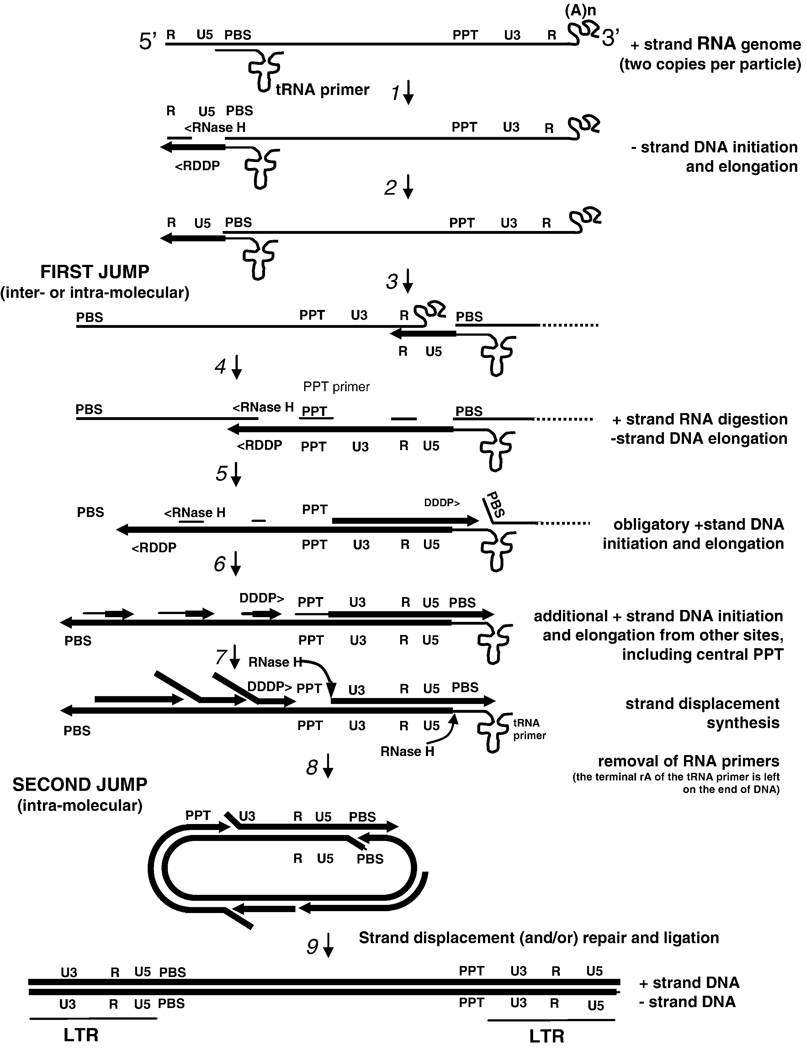
Figure 1.
Reverse transcription of the HIV-1 genome (with permission from Annual Review of Biochemistry). Each retroviral particle contains two copies of the RNA genome. Minus-strand DNA synthesis starts near the 5’ end of the plus-stand RNA genome using as a primer a host tRNAlys3 that anneals at the primer-binding site (PBS).
Step 1: Synthesis proceeds to the 5’ end of the RNA genome through the U5 region, ending at the R region at the 5’end, forming the “minus-strand strong stop DNA.” Step 2: DNA synthesis is accompanied by RNase H digestion of the RNA portion of the RNA-DNA hybrid product, thus exposing the single-strand DNA product. Step 3: This exposure facilitates hybridization with the R region at the 3’ end of the same, or the second RNA genome, a strand-transfer reaction known as the “first jump”. Step 4: When minus-strand elongation passes a polypurine rich region called the polypurine tract (PPT) region, a unique plus-strand RNA primer is formed by RNase H cleavage at its borders. Plus-strand synthesis then continues back to the U5 region using the minus-strand DNA as a template. Step 5: Meanwhile, minus-strand synthesis continues through the genome using the plus-strand RNA as a template, and removing the RNA template in its wake via RNase H activity. Step 6: The RNase H digestion products formed are presumed to provide additional primers for plus-strand synthesis at a number of internal locations along the minus-strand DNA. Step 7: PPT-initiated plus-strand DNA synthesis stops after copying the annealed portion of the tRNA to generate the plus-strand DNA form o f the PBS, forming the “plus-strand strong stop” product. The tRNA is then removed by the RNase H activity of RT. Step 8: This may facilitate annealing to the PBS complement on the minus-strand DNA, providing the complementarity for the “second jump.” DNA synthesis then continues. Step 9: Strand displacement synthesis by RT to the PBS and PPT ends, and/or repair and ligation of a circular intermediate produces a linear duplex with long terminal repeats (LTRs) at both ends.