Figure 4. Constitutively active Rac1 (RacV12) recovers transformed growth of PKCι RNAi PDAC cells in a MEK-dependent manner.
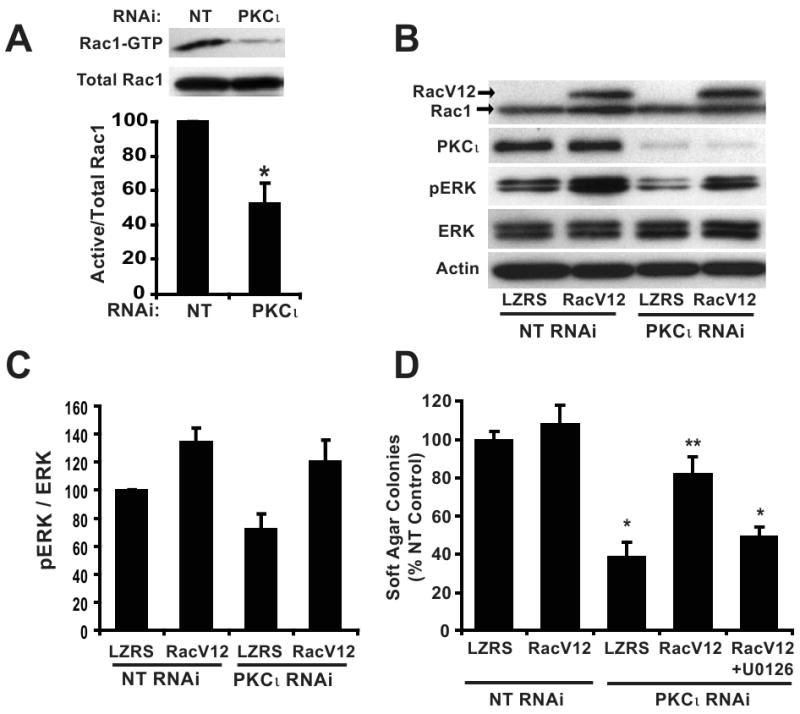
A) Panc-1 cells stably expressing NT or PKCι RNAi were assayed for Rac1 activity. Top panel, (Active) Rac1-GTP was precipitated from cell extracts with PAK-1 PBD agarose. Immunoblot analysis of precipitates and total cellular extracts (total Rac1) was performed using an anti-Rac1 antibody. Bottom panel, Quantitative, densitometric analysis of relative Rac1 activity (active Rac1/total Rac1). Mean +/- SEM is plotted, n=3. B) Panc-1 cells co-transfected with RNAi (NT or PKCι) and control vector (LZRS) or vector expressing RacV12 were subject to immunoblot analysis for expression of Rac1, PKCι, p-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), ERK1/2 and actin as a loading control. Arrows indicate migration of endogenous Rac1 and slower migrating myc-tagged RacV12. C) Quantitation of densitometric analysis of relative p-ERK1/2 to ERK1/2 expression. Mean +/- SEM is plotted, n=3. D) Expression of RacV12 recovers the inhibitory effect of PKCι RNAi on soft agar colony formation and requires MEK activity. +U0126= 10 μM U0126 was included in the assay media and agar; *= significantly different than control (NT & LZRS) and RacV12 reconstituted (PKCι RNAi & RacV12); **= significantly different than PKCι KD (PKCι RNAi & LZRS) and MEK-inhibited (PKCι RNAi & RacV12+U0126). Mean +/-SEM is plotted and represents two independent experiments.
