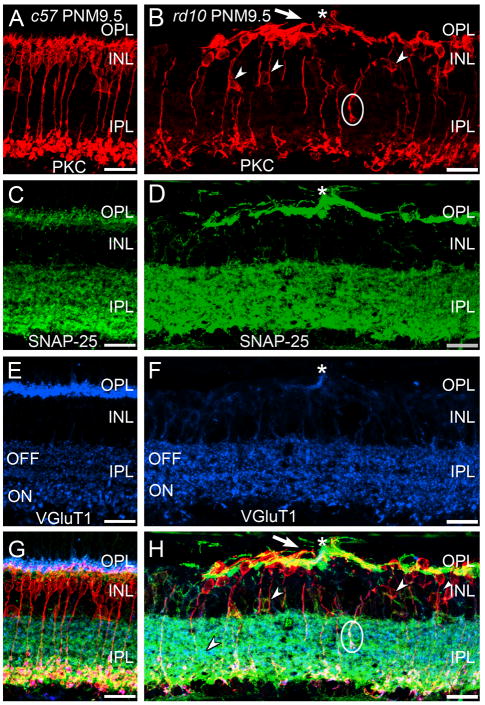
Figure 7. Immunostaining for PKC, SNAP-25 and VGluT1 in the C57BL/6 and rd10 retina.
A, C, E, G: Wild-type C57BL/6 (c57) retina at PNM9.5. A. Antibodies against protein kinase C-α (PKC) identify rod bipolar cells, which show normal morphology and stratification in the IPL. C. In c57 retina, the presynaptic SNARE protein SNAP-25 is found in the conventional and ribbon synapses of the OPL and IPL. E. VGluT1 expression in the C57BL/6 retina. G. Overlay of panels A, C and E. B, D, F, H: rd10 retina at PNM9.5. B. Although many rod bipolar cells are lost by PNM9.5 and most surviving rod bipolar cells have retracted their dendrites, rod bipolar cells located near surviving cone terminals extend abnormal, thickened dendrites (arrow) toward the surviving cone terminals (asterisk, see panel F). Many ectopic rod bipolar cell bodies (small arrowheads) and processes (circle) are present. Note the sparse plexus of rod bipolar cell terminals in the IPL. D. SNAP-25 labeling is highly elevated in the OPL but appears unchanged in the IPL. The cellular origin of the highly SNAP-25-positive processes in the outer retina is uncertain. F. A single VGluT1-positive terminal remains in this region of the OPL (asterisk). H. Overlay of panels B, D and F. Abnormal PKC-positive rod bipolar cell dendrites extend toward the surviving VGluT1-positive terminal (asterisk). Scale bar = 20 μm, all panels.