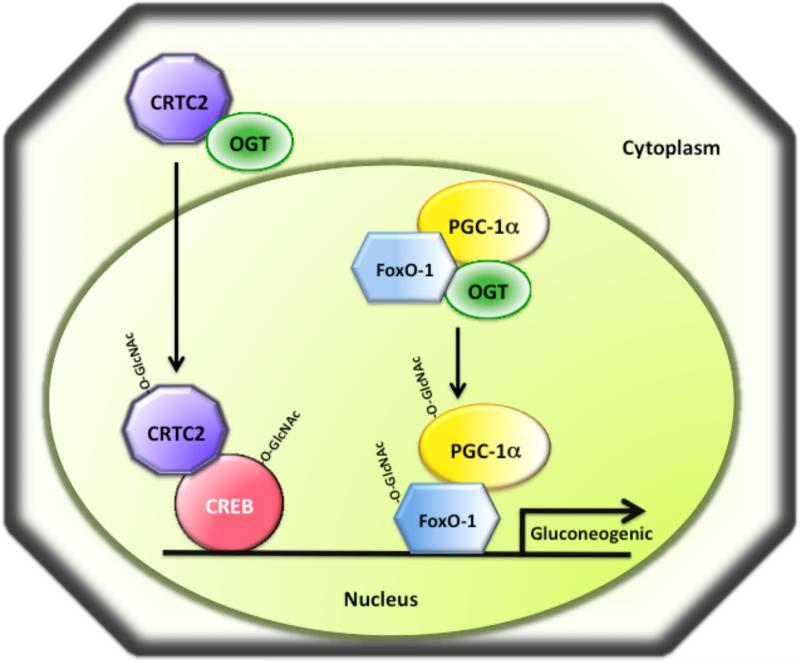
Fig. 7. O-GlcNAc modification regulates gluconeogenic gene expression in liver during diabetic conditions.
Chronic hyperglycemia or diabetes causes induction of gluconeogenic gene expression by O-GlcNAc modification of the transcription factors CREB and FoxO-1 and their co-activators CRTC2 and PGC-1α, respectively. O-GlcNAc modification of CRTC2 under diabetic conditions causes CRTC2 translocation into the nucleus where it interacts with CREB to activate gluconeogenic gene expression. The co-activator PGC-1α has been demonstrated to be O-GlcNAc modified and to recruit OGT to FoxO-1, promoting O-GlcNAc modification of FoxO-1 and activation of gluconeogenic genes.