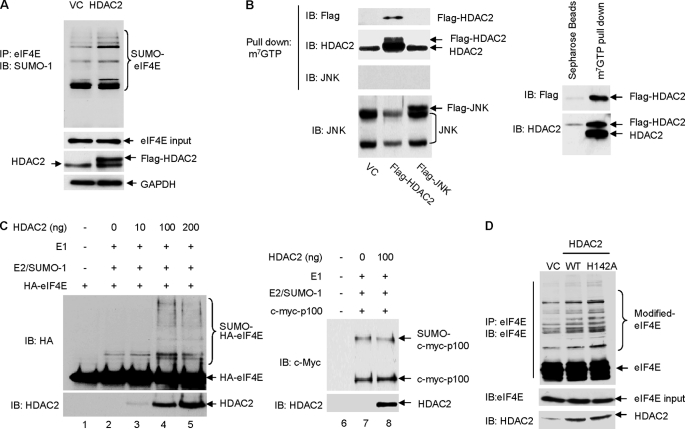
FIGURE 2.
HDAC2 stimulates eIF4E sumoylation. A, overexpression of HDAC2 induces eIF4E sumoylation. The HCT-116 cells were transfected with FLAG-HDAC2 or control vectors (VC). Sumoylation of eIF4E was evaluated by immunoprecipitation (IP) of the whole cell lysates with anti-eIF4E followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-SUMO-1. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. B, HDAC2 but not JNK1 is associated with cap-bound translation initiation complex. The HCT-116 cells were transfected with empty vector or FLAG-HDAC2 or FLAG-JNK1. 48 h after transfection, the cells were harvested for the pulldown assays. Left panel, the cap-bound HDAC2 was eluted from the 7-methyl-GTP (m7GTP)-Sepharose resin using 7-methyl-GDP (m7GDP) and detected by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG or anti-HDAC2. Right panel, immunoprecipitation with Sepharose beads was included as the experimental control. C, the addition of purified recombinant HDAC2 protein directly stimulates in vitro sumoylation of eIF4E but not NF-κB2/p100. 1 μl of in vitro translated human influenza HA-tagged eIF4E or c-Myc-p100 was used as SUMO substrate. 0–200 ng of human recombinant HDAC2 protein (Biomol International) was added to the in vitro sumoylation reaction mixture as labeled in the figure. Sumoylated and non-sumoylated HA-eIF4E and c-Myc-p100 were detected by immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-c-Myc, respectively. The addition of HDAC2 was verified by immunoblotting with anti-HDAC2. D, overexpression of HDAC2 and HDAC2 deacetylase-dead mutant (HDAC2-H142A) on eIF4E sumoylation in HCT-116 cells. WT, wild type.