FIGURE 6.
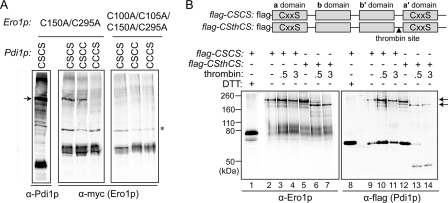
Ero1p preferentially forms a mixed-disulfide intermediate with the a domain of Pdi1p. A, formation of mixed-disulfide intermediates between Ero1p(C150A/C295A) (with a Myc epitope tag) and Pdi1p mutants Pdi1p(CSCS), Pdi1p(CSCC), and Pdi1p(CCCS). NEM-modified yeast cell lysates were resolved by non-reducing SDS-PAGE, and mixed-disulfide intermediates between Ero1p and Pdi1p were identified by Western blotting with either anti-Pdi1p or anti-Myc. Catalytically inactive Ero1p(C100A/C105A/C150A/C295A) was used as a negative control. An arrow denotes the mixed-disulfide complexes between mutant Ero1p and a subset of Pdi1p variants. Other bands in the leftmost (α-Pdi1p) lane are mixed-disulfide complexes between Pdi1p(CSCS) and other proteins (high molecular weight bands) or free Pdi1p(CSCS) (intense lower band). The asterisk indicates a nonspecific background band that does not disappear upon reduction (not shown). B, thrombin digestion of the Pdi1p(CSCS)-Ero1p(C150A/C295A) mixed-disulfide intermediate. To enable dissection of Pdi1p(CSCS), a thrombin site was introduced into the segment linking the b′ and a′ domains to generate the construct Pdi1p(CSthCS). Mixed-disulfide intermediates were isolated under non-reducing conditions from cells expressing a FLAG-epitope-tagged Pdi1p by affinity to anti-FLAG beads. Purified Pdi1p(CSCS)- and Pdi1p(CSthCS)-Ero1p(C150A/C295A) mixed-disulfide complexes were digested by thrombin, and association of the Pdi1p fragments with Ero1p was analyzed by immunoblotting with either anti-Ero1p or anti-FLAG. Arrows highlight the major Pdi1p-Ero1p mixed-disulfide complexes observed before (top) and after (bottom) thrombin cleavage.