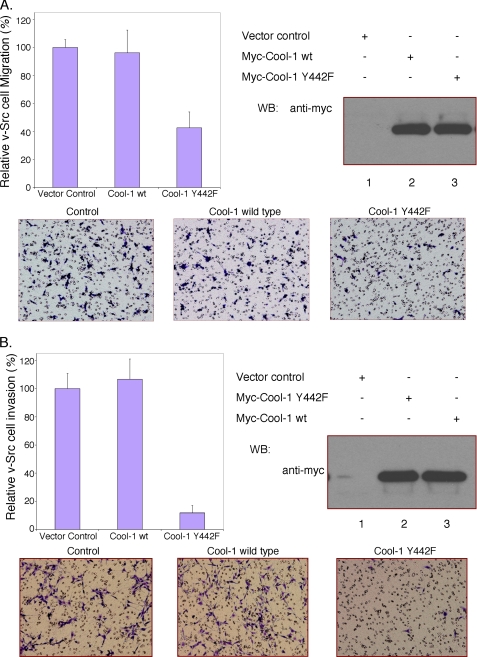
FIGURE 4.
The phosphorylation of Cool-1 is important for the migration and invasive activity of v-Src-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. A, viral-Src-transformed NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with empty vector (control), Myc-tagged wild-type Cool-1, or the Cool-1 Y442F mutant. The cells were cultured for 24 h and then scored for their ability to migrate as described in Fig. 1. Top-left panel, the number of cells that migrated through the filters for the wild-type Cool-1- and the Cool-1 Y442F-expressing cells were counted and compared with the number of control cells counted (set at 100%). The results from three experiments were averaged and plotted. The error bars indicate ± S.D. Top-right panel, Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot analysis to determine the expression levels of the Myc-tagged Cool-1 proteins. Bottom panels, microscopic images of the migration assays shown in the top-left panel. The cells are visualized by GIEMSA staining (dark blue). The round (clear) circles are not cells but represent the holes in the filter. B, viral-Src-transformed NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with empty vector, Myc-tagged wild-type Cool-1, or the Cool-1 Y442F mutant. The cells were cultured for 24 h and then scored for invasiveness as described under “Experimental Procedures.” At least 100 cells were examined for each condition. The cells counted for the control were set at 100%. Top-left panel, results from three experiments were averaged and plotted. The error bars indicate ± S.D. Top-right panel, cell lysates were analyzed to determine the expression levels of the Myc-tagged Cool-1 proteins. Bottom panels, microscopic images of the invasion assays shown in the top-left panel. The cells are visualized by GIEMSA staining (dark purple).