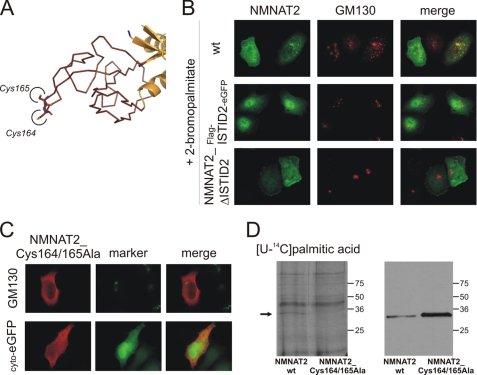
FIGURE 6.
Cysteine-specific palmitoylation within ISTID2 anchors NMNAT2 at the Golgi complex. A, the tertiary structure prediction for NMNAT2 suggests that Cys164 and Cys165 are located at the very tip of ISTID2. B, FLAG-tagged wild-type (wt) NMNAT2, the ISTID2 deletion mutant (NMNAT2_ΔISTID2), or the FLAG-ISTID2-eGFP fusion protein was overexpressed in HeLa S3 cells in the presence of 25 μm 2-BP to inhibit protein palmitoylation. The endogenous 2-BP-resistant Golgi marker GM130 was immunostained for comparison. C, substitution of Cys164 and Cys165 with alanine caused relocalization of NMNAT2 to the cytoplasm. After overexpression in HeLa S3 cells, the double mutant NMNAT2_Cys164/165Ala was visualized by FLAG immunocytochemistry. The endogenous Golgi marker GM130 or coexpressed cytosolic eGFP (cyto-eGFP) was used for comparison. D, shown is the in vivo palmitoylation of NMNAT2. HeLa S3 cells overexpressing FLAG-tagged wild-type NMNAT2 or mutant NMNAT2_Cys164/165Ala were incubated with [14C]palmitic acid. Cell extracts were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to autoradiography (left panel) and FLAG immunoblot analyses (right panel). The arrow indicates a radiolabeled band (∼34 kDa) that corresponds to FLAG-tagged wild-type NMNAT2.