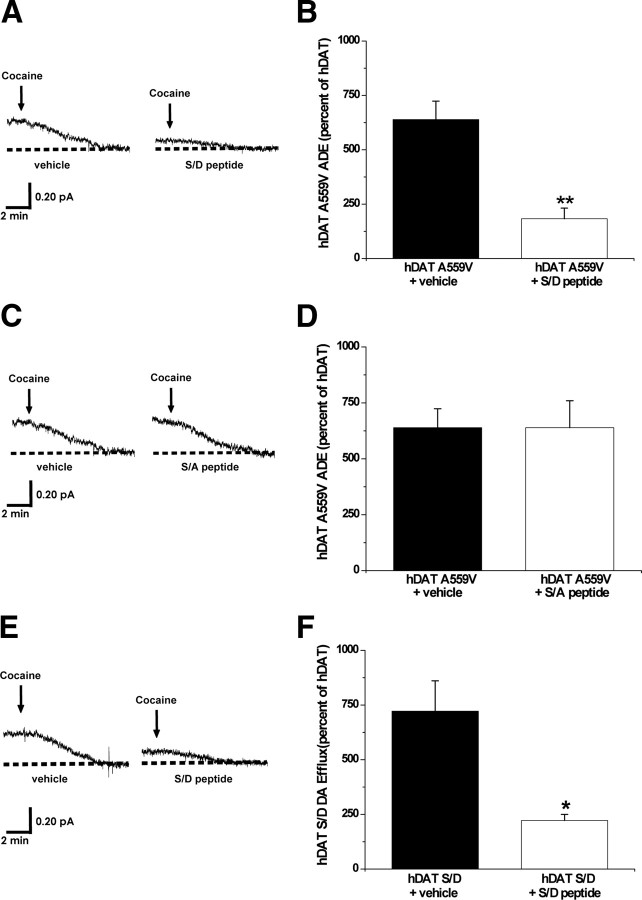
Figure 4.
Phosphorylated DAT N terminus forms critical interactions that underlie the ability of A559V to cause ADE. A, Representative oxidative currents in hDAT A559V cells following whole-cell perfusion with vehicle (left) or a peptide corresponding to the first 27 residues of hDAT with the N-terminal serines substituted for aspartates (hDAT S/D peptide, right). Arrows indicate addition of cocaine. Cells were whole-cell patch clamped and perfused for 10 min to allow for loading of 2 mm DA and either 3 μm hDAT S/D peptide or vehicle control, and measured for ADE as described in Materials and Methods. B, Data reported as mean amperometric current ± SEM in hDAT A559V cells expressed as a percentage of current recorded in hDAT cells both in control conditions (n = 3) and with hDAT S/D peptide (n = 5) (t = 5.9, df = 6, p = 0.001, Student's t test). C, Representative oxidative currents in hDAT A559V cells following whole-cell perfusion with vehicle (left) or a peptide corresponding to the first 27 residues of hDAT with the N-terminal serines substituted for alanines (hDAT S/A peptide, right). Cells were whole-cell patch clamped and perfused as described above. D, Data reported as mean amperometric current ± SEM in hDAT A559V cells expressed as a percentage of current recorded in hDAT cells both in control conditions (n = 3) and with hDAT S/A peptide (n = 3) (t = 0, df = 4, p = 1.0, Student's t test). E, Representative oxidative currents in hDAT S/D cells following whole-cell perfusion with vehicle (left) or hDAT S/D peptide (right). Cells were whole-cell patch clamped and perfused as described above. F, Data reported as mean amperometric current ± SEM in hDAT S/D cells expressed as a percentage of current recorded in hDAT cells both in control conditions (n = 3) and with hDAT S/D peptide (n = 3) (t = 3.5, df = 4, p = 0.02, Student's t test). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.