Figure 6.
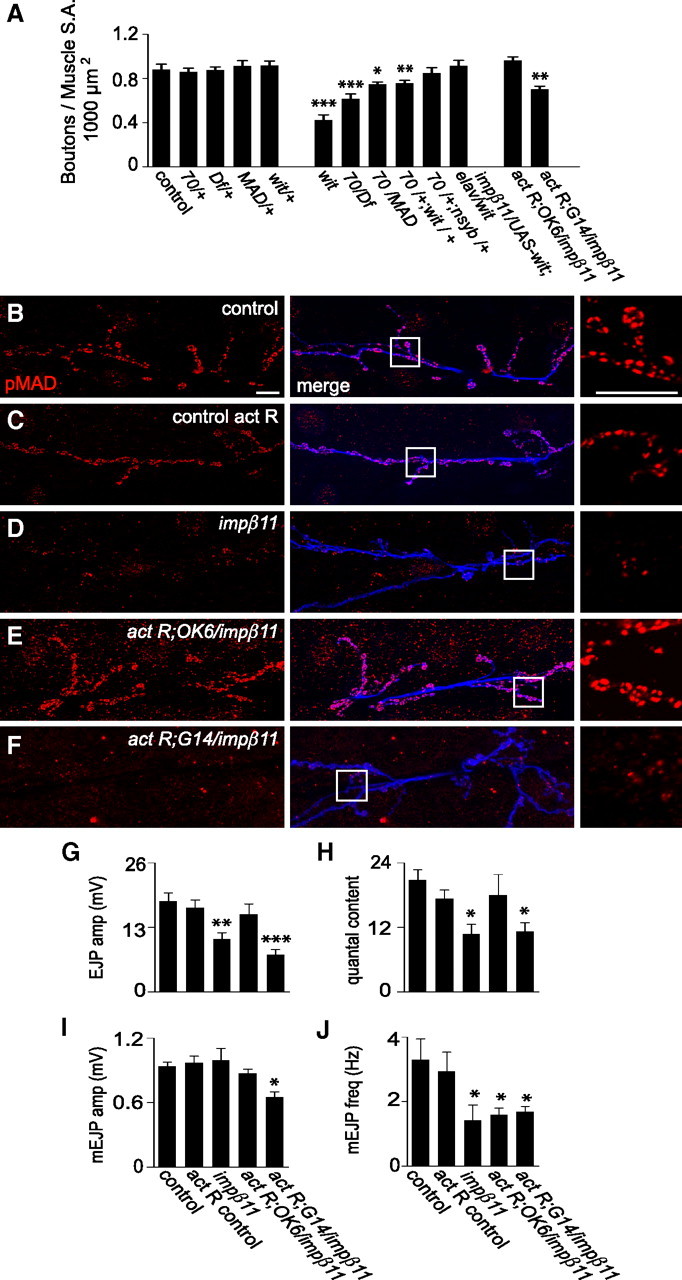
Genetic interaction of impβ11 and the BMP pathway. A, BMP pathway mutants and impβ11 interact to form fewer synaptic boutons on muscles 6 and 7. Bouton counts were normal in heterozygotes of impβ1170 or the indicated alleles of BMP pathway mutants but reduced in larvae heterozygous for both impβ1170 and either MAD10 or witHA1, an interaction not seen with n-sybF-33R. Bouton number was rescued by presynaptic expression of UAS-wit in impβ1170; witHA1 transheterozygotes. In addition, neuronal (but not muscle) expression of constitutively activated BMP receptors (UAS-tkvact, saxact) restored bouton number in an impβ11 mutant background. B–F, Representative confocal images of anti-pMAD (red) and anti-HRP (blue) immunoreactivity to illustrate the effects of the constitutively activated BMP receptors on pMAD levels. Scale bars, 10 μm. In control larvae, the activated receptors driven in motor neurons did not appreciably increase pMAD (C), but in impβ11 larvae pMAD levels were restored (E). When activated receptors were expressed in impβ11 muscle, pMAD staining was not restored (F). G–J, EJP amplitude and quantal content, but not mini frequency, were restored to control levels by the activated BMP receptors expressed in motor neurons but not in muscle. Recordings were conducted in 0.6 mm Ca2+ HL3; n ≥ 6 for each genotype. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001 compared to control. Genotypes are as follows: control (y,w; FRT42D), 70/+ (w;FRT42D, impβ1170/+), MAD/+ (MAD10/+), wit/+ (witHA1/+), wit (witA12/witB11), 70/Df (FRT42D, impβ1170/ Df), 70/MAD (FRT42D, impβ1170/ mad10), 70/+;wit/+ (FRT42D, impβ1170/+; witHA1/+), 70/+;n-syb/+ (FRT42D, impβ1170/+; n-sybF-33R/+), 70/UAS-wit;elav/wit (FRT42D, impβ1170/UAS-wit; elav-GAL4/witHA1), control act R (UAS-tkvact, UAS-saxact; OK6-GAL4/+), act R;OK6/ impβ11 (UAS-tkvact, UAS-saxact; FRT42D, impβ1170, OK6-GAL4/Df), act R;G14/ impβ11 (UAS-tkvact, UAS-saxact; FRT42D, impβ1170,G14-GAL4/Df).
