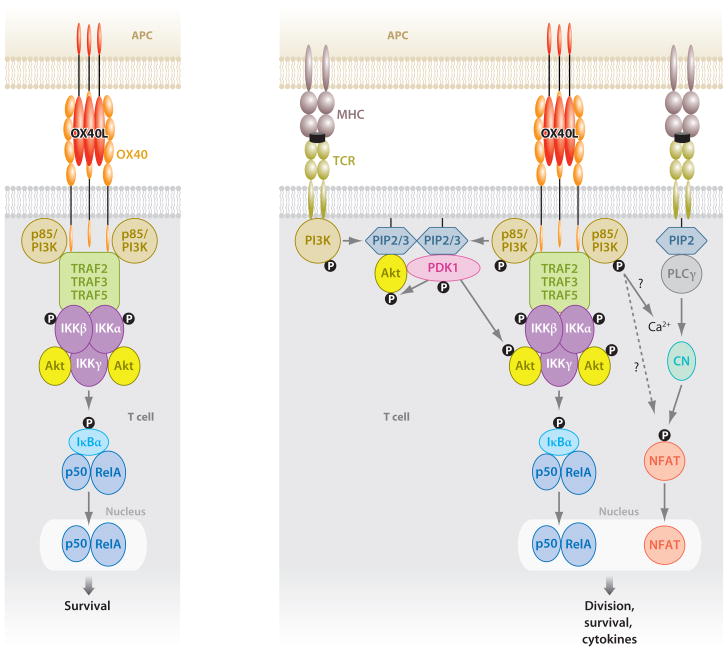
Figure 1.
OX40 acts as both an independent signaling entity (left) and an entity augmenting antigen-driven TCR signaling (right). Binding of OX40L results in trimerization of OX40 monomers and the recruitment of TRAF2, 3, and 5. The sequence of events resulting in a functional OX40 signaling complex is not yet clear, but IKKα, IKKβ, IKKγ, the p85 subunit of PI3K, and Akt are found with the TRAF adaptors. The signalosome can result in phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα, leading to activation of NF-κB1 and entry of p50 and RelA into the nucleus. This is sufficient to provide survival signals to T cells in the absence of antigen recognition. NIK is most likely also recruited into the complex, although this has not been visualized at present. If NIK is recruited, this likely leads to activation of NF-κB2, which might also be necessary for transmitting survival signals. In this scenario without antigen recognition, PI3K and Akt are not activated. With antigen signaling, OX40 synergizes with the TCR to promote strong Akt phosphorylation, likely due to localization of the OX40 signalosome with PDK1 recruited by the TCR. TCR signals initiate intracellular Ca2+ influx, leading to NFAT dephosphorylation and nuclear entry. Through a mechanism not yet elucidated, OX40 synergizes with this process to allow greater Ca2+ influx and nuclear accumulation of NFAT. The combined antigen and OX40 signals in T cells can enhance expression of molecules such as survivin, cyclin A, cyclin-dependent kinases, Bcl-2 antiapoptotic molecules, cytokines, and cytokine receptors, as well as suppress Foxp3 and CTLA4 expression. (Abbreviations: TRAF, TNFR-associated factor; PI3K, PI-3-kinase; NIK, NF-κB-inducing kinase; IKKs, IκB kinases; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cell; PDK1, 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; CTLA4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte–associated antigen-4; PIP2/3, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate/3,4,5-trisphosphate; CN, calcineurin; PLCγ, phospholipase Cγ.)