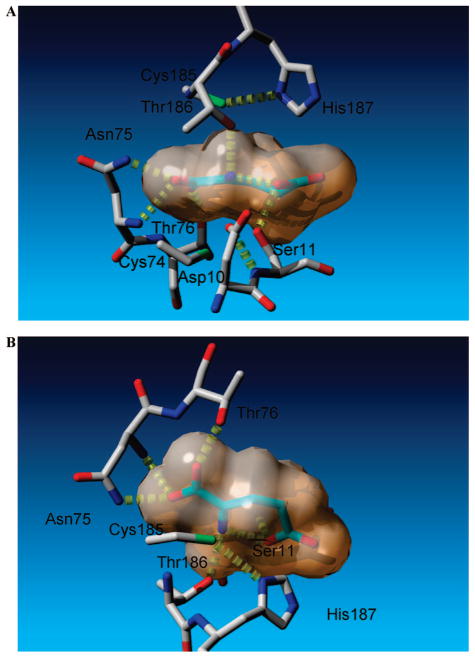
Figure 3.
Selective active-site contacts between glutamate carbanion and glutamate racemase. Glutamate racemase carbons are shown in gray, while those of glutamate carbanion are shown in light green hues. The van der Waals surface of the glutamate carbanion is indicated. Hydrogen bonds are depicted in yellow. (A) View looking down the NH3–Cα bond of the planar glutamate carbanion. The two catalytic acid/bases (Cys185 and Cys74) are shown above and below the plane of the carbanion, respectively. (B) Cyclic nature of the glutamate carbanion, which forms an intramolecular hydrogen bond between γ-carboxylate oxygen and NH3+.