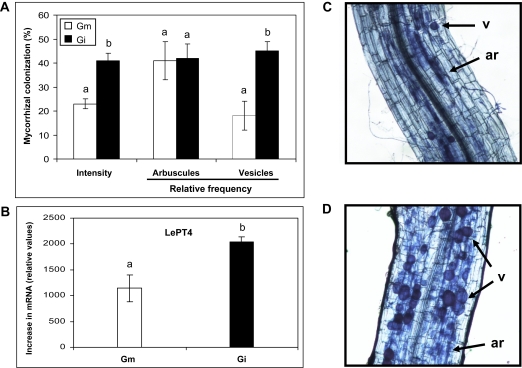
Fig. 1.
Mycorrhizal colonization and expression analysis of the marker gene LePT4 of tomato roots inoculated with G. mosseae or G. intraradices. (A) Intensity of mycorrhizal colonization by G. mosseae (Gm) or G. intraradices (Gi), and relative frequency of arbuscules and vesicles. (B) Gene expression analysis by real-time qPCR for the mycorrhizal marker gene LePT4. Data points represent the means of five (A) or three (B) replicates (±SE). Data not sharing a letter in common differ significantly (P <0.01) according to Fisher's LSD test. The right-hand panels show photographs of root samples after trypan blue staining. (C) Glomus mosseae colonizes the root cortex to a lower extent, forming a large number of arbuscules but a limited number of vesicles. (D) Glomus intraradices extensively colonize the root cortex forming arbuscules and a large number of vesicles. Arrows indicate arbuscules (ar) and vesicles (v).