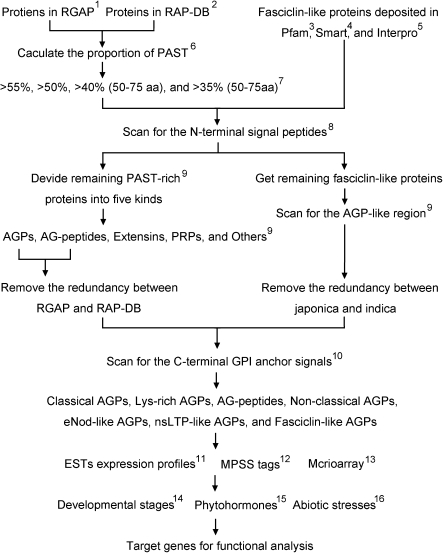
Fig. 1.
The workflow and parameters of AGP identification and data mining. 1, RGAP, Rice Genome Annotation Project; 2, RAP-DB, Rice Annotation Project Database; 3, PF02469 at http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/; 4, SM00554 at http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/; 5, IPR000782 at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/; 6, run a Perl script that divides proteins into several parts according to their amino acid composition; 7, aa, the length of candidate proteins in amino acids; 8, signal peptide prediction, http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/; 9, the criteria to separate different kinds of HRGPs are detailed in Materials and methods; 10, GPI anchor signal prediction, http://mendel.imp.ac.at/gpi/plant_server.html; 11, EST expression profiles from UniGene at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/unigene/; 12, MPSS tags, http://mpss.udel.edu/rice/; 13, the absolute signal values were downloaded at http://signal.salk.edu/cgi-bin/RiceGE; 14, GSE6893, expression at various developmental stages; 15, GSE661, expression under ABA and GA treatments; 16, GSE6901, expression under abiotic stresses treatments.