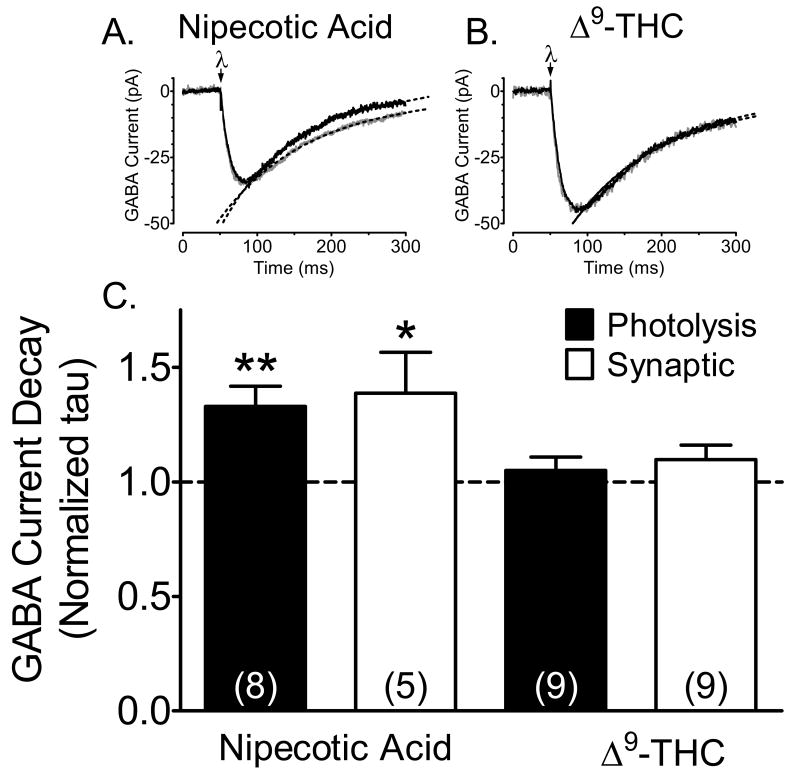
Figure 4.
Δ9-THC acts presynaptically to reduce GABAergic neurotransmission in the hippocampus. A. Effect of the competitive GABA uptake inhibitor nipecotic acid (10 μM, gray line) on averaged (n = 6-9 individual sweeps) inward currents evoked by CNB-GABA photolysis (uv laser flash applied at λ) in a CA1 pyramidal neuron. The control sweep is shown in black. Also shown (dashed lines) are single exponential curves fitted to the decay phase of the currents that were used to calculate the decay time constants (tau). Note that nipecotic acid significantly increased the tau value in this cell (control tau =100.8 ms, 95% C.I. = 99.0-102.7 ms; nipecotic acid tau =120.9 ms, 95% C.I. = 118.3-123.5 ms). Currents shown here and in B are scaled to the same amplitude. B. Lack of an effect of Δ9-THC (10 μM, gray line) on photolysis-evoked GABA current decay in a CA1 pyramidal neuron (control tau = 116.8 ms, 95% C.I. = 115.0-118.7 ms; Δ9-THC tau = 116.9 ms, 95% C.I. = 114.4-119.5 ms). C. Summary of the effect of nipecotic acid and Δ9-THC on decay tau values for GABA currents evoked by synaptic stimulation and photolysis of CNB caged GABA. Values represent ratios of the tau value acquired after drug application to that obtained during the control period. Note that Δ9-THC did not significantly affect synaptic or photolysis-evoked GABA current decay, whereas nipecotic acid prolonged the tau values for each of these currents. *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001, paired t-test. These data indicate that GABA uptake was unaffected by Δ9-THC under the present recording conditions.