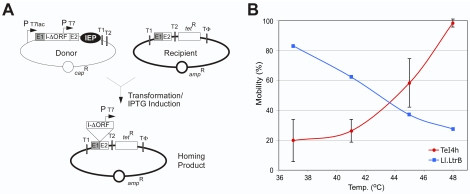
Figure 4. TeI4h intron mobility assays.
(A) E. coli genetic assay of intron mobility. The CapR donor plasmid uses a T7lac promoter (PT7lac) to express a ΔORF intron (I-ΔORF) with short flanking 5′ and 3′ exons (E1 and E2, respectively) and the IEP downstream of E2. The intron, which carries a T7 promoter (PT7) in DIVb, integrates into a target site (ligated E1–E2 sequences) cloned in an AmpR recipient plasmid upstream of a promoterless tetR gene, thereby activating that gene. The donor and recipient plasmids are derivatives of pACD2X and pBRR-tet, respectively (see Materials and Methods). The assays are done in E. coli HMS174(DE3), which contains an IPTG-inducible T7 RNA polymerase, with intron expression induced with 500 µM IPTG for 1 h at different temperatures. Mobility efficiencies are calculated as the ratio of (TetR+AmpR)/AmpR colonies. (B) Mobility efficiency of the TeI4h-ΔORF (blue) and Ll.LtrB-ΔORF (red) introns as a function of induction temperature. The donor plasmid for the Ll.LtrB-ΔORF intron was pACD2X [47].