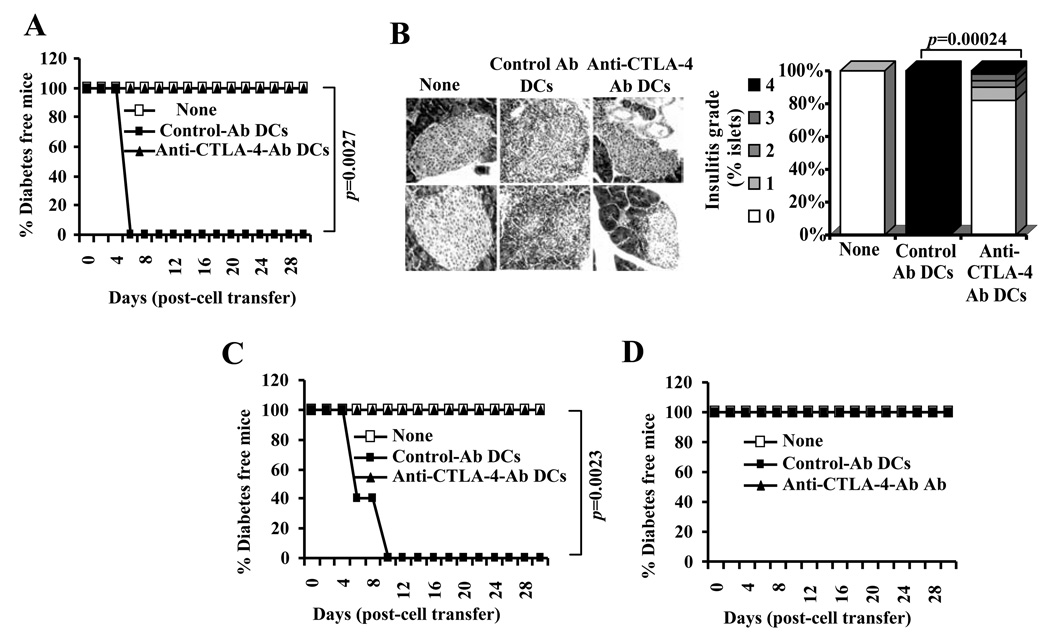
FIGURE 11.
DC directed enhanced CTLA-4 engagement alters the function of diabetogenic T cells. A) Purified CD4+ T cells from BDC2.5 TCR-Tg mice were incubated with BDC peptide pulsed control or anti-CTLA-4 Ab coated DCs for 4 days. T cells from these cultures were injected i.v. into 4-week-old male NOD mice (1×106/mouse; n=5/group), monitored for blood glucose levels, and the results are plotted as % diabetes free mice at different time-points. B) Pancreatic tissues obtained from an additional set of mice on day 5 post-T cell transfer were examined for insulitis as described under materials and methods. Representative sections with different grades of insulitis (left panel) and bar diagram showing the percentage of islets with different grades of insulitis in each group are shown (right panel). C and D) In parallel experiments, purified CD4+ T cells from BDC2.5 TCR-Tg mice were incubated with BDC peptide pulsed control or anti-CTLA-4 Ab coated DCs in the presence of recombinant IL-2 (10 U/ml) (panel C) or TGF-β1 (1 ng/ml) (panel D) for 4 days, T cells from these cultures were injected i.v. into male NOD mice (n=5/group) and monitored for blood glucose levels as described for panel A, and the results are plotted as % diabetes free mice at different time-points. Statistical significance of disease free status was assessed by log-rank test comparing control Ab coated DC group with anti-CTLA-4 Ab coated DC group.