Abstract
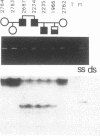
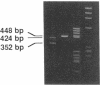
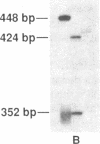
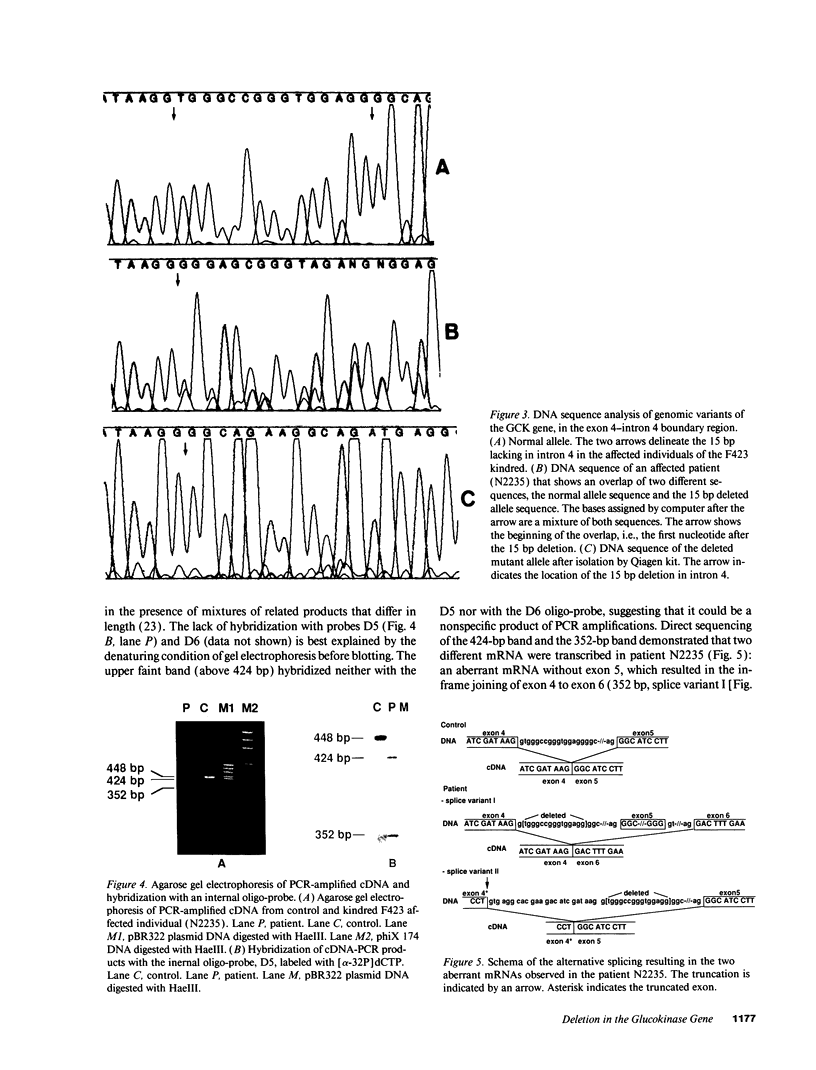
Missense and nonsense mutations in the glucokinase gene have recently been shown to result in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), a subtype of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with early age of onset. Glucokinase catalyzes the formation of glucose-6-phosphate and is involved in the regulation of insulin secretion and integration of hepatic intermediary metabolism. Nucleotide sequence analysis of exon 4 and its flanking intronic regions of the glucokinase gene, in four hyperglycemic individuals of a MODY family, revealed a deletion of 15 base pairs, which removed the t of the gt in the donor splice site of intron 4, and the following 14 base pairs. This deletion resulted in two aberrant transcripts, which were analyzed by reverse transcription of RNA from lymphoblastoid cells obtained from a diabetic patient. In one of the abnormal transcripts, exon 5 is missing, while in the other, the activation of a cryptic splice site leads to the removal of the last eight codons of exon 4. This intronic deletion in a donor splice site seems to cause a more severe form of glucose intolerance, compared with point mutations described in glucokinase. This might be due to a more pronounced effect on insulin secretion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett A. H. Diabetes, race and genes. Diabet Med. 1989 Jan-Feb;6(1):78–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1989.tb01144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Concordet J. P., Kaplan J. C., Kahn A. Illegitimate transcription: transcription of any gene in any cell type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2617–2621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Gilgenkrantz H., Hugnot J. P., Hamard G., Lambert M., Récan D., Akli S., Cometto M., Kahn A., Kaplan J. C. Illegitimate transcription. Application to the analysis of truncated transcripts of the dystrophin gene in nonmuscle cultured cells from Duchenne and Becker patients. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1161–1166. doi: 10.1172/JCI115417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajans S. S. Scope and heterogeneous nature of MODY. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jan;13(1):49–64. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froguel P., Vaxillaire M., Sun F., Velho G., Zouali H., Butel M. O., Lesage S., Vionnet N., Clément K., Fougerousse F. Close linkage of glucokinase locus on chromosome 7p to early-onset non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):162–164. doi: 10.1038/356162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froguel P., Velho G., Cohen D., Passa P. Strategies for the collection of sibling-pair data for genetic studies in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1991 Sep;34(9):685–685. doi: 10.1007/BF00401001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froguel P., Zouali H., Vionnet N., Velho G., Vaxillaire M., Sun F., Lesage S., Stoffel M., Takeda J., Passa P. Familial hyperglycemia due to mutations in glucokinase. Definition of a subtype of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993 Mar 11;328(10):697–702. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199303113281005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidh-Jain M., Takeda J., Xu L. Z., Lange A. J., Vionnet N., Stoffel M., Froguel P., Velho G., Sun F., Cohen D. Glucokinase mutations associated with non-insulin-dependent (type 2) diabetes mellitus have decreased enzymatic activity: implications for structure/function relationships. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattersley A. T., Turner R. C., Permutt M. A., Patel P., Tanizawa Y., Chiu K. C., O'Rahilly S., Watkins P. J., Wainscoat J. S. Linkage of type 2 diabetes to the glucokinase gene. Lancet. 1992 May 30;339(8805):1307–1310. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91958-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri H., Asano T., Ishihara H., Inukai K., Anai M., Miyazaki J., Tsukuda K., Kikuchi M., Yazaki Y., Oka Y. Nonsense mutation of glucokinase gene in late-onset non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1992 Nov 28;340(8831):1316–1317. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92494-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knebelmann B., Boussin L., Guerrier D., Legeai L., Kahn A., Josso N., Picard J. Y. Anti-Müllerian hormone Bruxelles: a nonsense mutation associated with the persistent Müllerian duct syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3767–3771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knebelmann B., Deschenes G., Gros F., Hors M. C., Grünfeld J. P., Zhou J., Tryggvason K., Gubler M. C., Antignac C. Substitution of arginine for glycine 325 in the collagen alpha 5 (IV) chain associated with X-linked Alport syndrome: characterization of the mutation by direct sequencing of PCR-amplified lymphoblast cDNA fragments. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;51(1):135–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroux C., Mazure N., Martin P. Mutations away from splice site recognition sequences might cis-modulate alternative splicing of goat alpha s1-casein transcripts. Structural organization of the relevant gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6147–6157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson M. A. Glucokinase gene structure. Functional implications of molecular genetic studies. Diabetes. 1990 May;39(5):523–527. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M. Glucokinase as glucose sensor and metabolic signal generator in pancreatic beta-cells and hepatocytes. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):647–652. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Matschinsky F. M. New perspectives on pancreatic islet glucokinase. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):E1–13. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.1.E1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S. S. Mapping genes in diabetes. Genetic epidemiological perspective. Diabetes. 1990 Nov;39(11):1315–1319. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.11.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson B. L., Cote G. J., Berget S. M. Exon definition may facilitate splice site selection in RNAs with multiple exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):84–94. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert J. J., Deschamps I., Chevenne D., Roger M., Mogenet A., Boitard C. Relationship between first-phase insulin secretion and age, HLA, islet cell antibody status, and development of type I diabetes in 220 juvenile first-degree relatives of diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 1991 Aug;14(8):718–723. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.8.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. G., Bobrow M., Bentley D. R. Point mutations in the dystrophin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2331–2335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuraba H., Eng C. M., Desnick R. J., Bishop D. F. Invariant exon skipping in the human alpha-galactosidase A pre-mRNA: Ag+1 to t substitution in a 5'-splice site causing Fabry disease. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):643–650. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel M., Froguel P., Takeda J., Zouali H., Vionnet N., Nishi S., Weber I. T., Harrison R. W., Pilkis S. J., Lesage S. Human glucokinase gene: isolation, characterization, and identification of two missense mutations linked to early-onset non-insulin-dependent (type 2) diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7698–7702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel M., Patel P., Lo Y. M., Hattersley A. T., Lucassen A. M., Page R., Bell J. I., Bell G. I., Turner R. C., Wainscoat J. S. Missense glucokinase mutation in maturity-onset diabetes of the young and mutation screening in late-onset diabetes. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):153–156. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talerico M., Berget S. M. Effect of 5' splice site mutations on splicing of the preceding intron. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6299–6305. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velho G., Froguel P., Clement K., Pueyo M. E., Rakotoambinina B., Zouali H., Passa P., Cohen D., Robert J. J. Primary pancreatic beta-cell secretory defect caused by mutations in glucokinase gene in kindreds of maturity onset diabetes of the young. Lancet. 1992 Aug 22;340(8817):444–448. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91768-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vionnet N., Stoffel M., Takeda J., Yasuda K., Bell G. I., Zouali H., Lesage S., Velho G., Iris F., Passa P. Nonsense mutation in the glucokinase gene causes early-onset non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):721–722. doi: 10.1038/356721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]