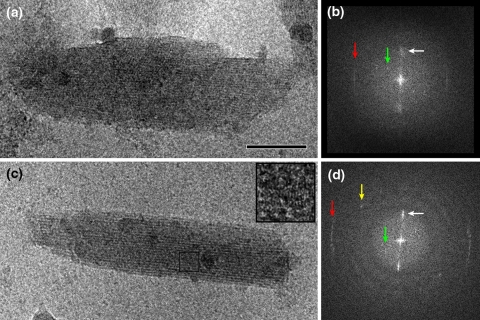
Fig. 4.
Analysis of the interior of the chlorosome of Chlorobaculum tepidum. a Image of an unstained, ice-embedded chlorosome from the wild-type. b Calculated diffraction pattern from the image of frame a. A bright but unsharp reflection spot (white arrow) indicates an average spacing between lamellae of 2.1 nm, which is also directly visible in the image of frame a. A sharp layer line at 1.25 nm (red arrow) indicates a specific internal repeating distance of 1.25 nm of the lamellae, caused by a specific packing of BChls. A thin but distinct reflection at 3.3 nm (green arrow) is assigned to a spacing of protein molecules of the baseplate. c Image of an unstained, ice-embedded chlorosome from the bclQRU mutant. d Calculated diffraction pattern from the image of c. The white and green arrows indicate structural elements as in the pattern of frame b. The sharp layer line (red arrow) now indicates a specific internal repeating distance of 0.83 nm, instead of 1.25 nm as in the wild-type. The yellow arrow marks a sharp reflection that hints at another type of spacing (1.1 nm), likely in the baseplate. Size bar equals 50 nm for frames a and c