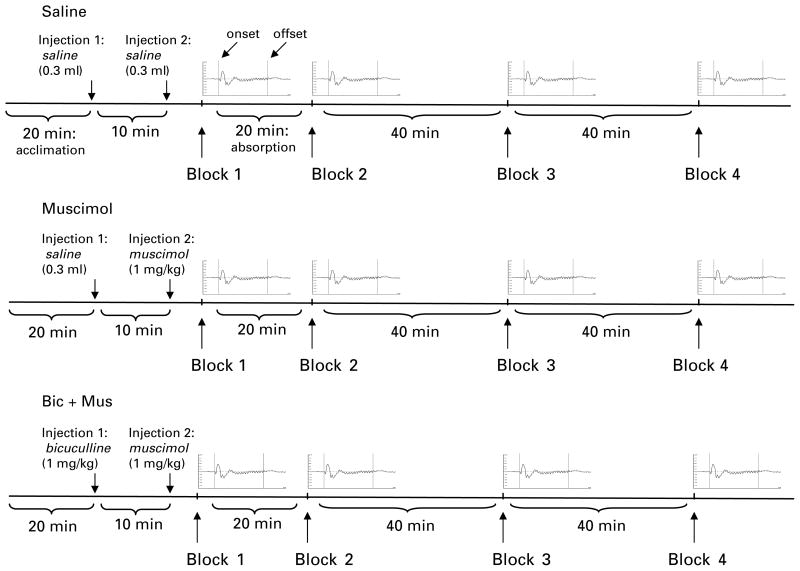
Fig. 1.
Electrophysiological recording procedure. The three drug conditions were performed at least 24 h apart. Each rat was allowed a 20-min acclimation period followed by the first injection. The first injection was saline (0.3 ml s.c.) in the saline and muscimol conditions and bicuculline (1.0 mg/kg s.c.) in the bicuculline + muscimol (Bic + Mus) condition. A 10-min delay was followed by a second injection of saline (0.3 ml in saline condition) or muscimol (1 mg/kg in both the muscimol and bicuculline + muscimol conditions) and then immediately by the first block of auditory steady-state responses (ASSRs) (block 1, time 0). Exactly 20 min (absorption period, indicated in saline condition) following the second injection, the second block of trials was presented. Four blocks of 200 trials of 500-ms click train stimuli were presented at 0 min (block 1), 20 min (block 2), 60 min (block 3), and 100 min (block 4) after the second injection. An average ASSR waveform is presented here to represent each block of trials. Amplitude (mV) is on the y axis and trial duration (ms) is on the x axis. The two vertical lines in each average represent onset (left, 0 ms) and offset (right, 500 ms) of the click train (labelled in saline condition).