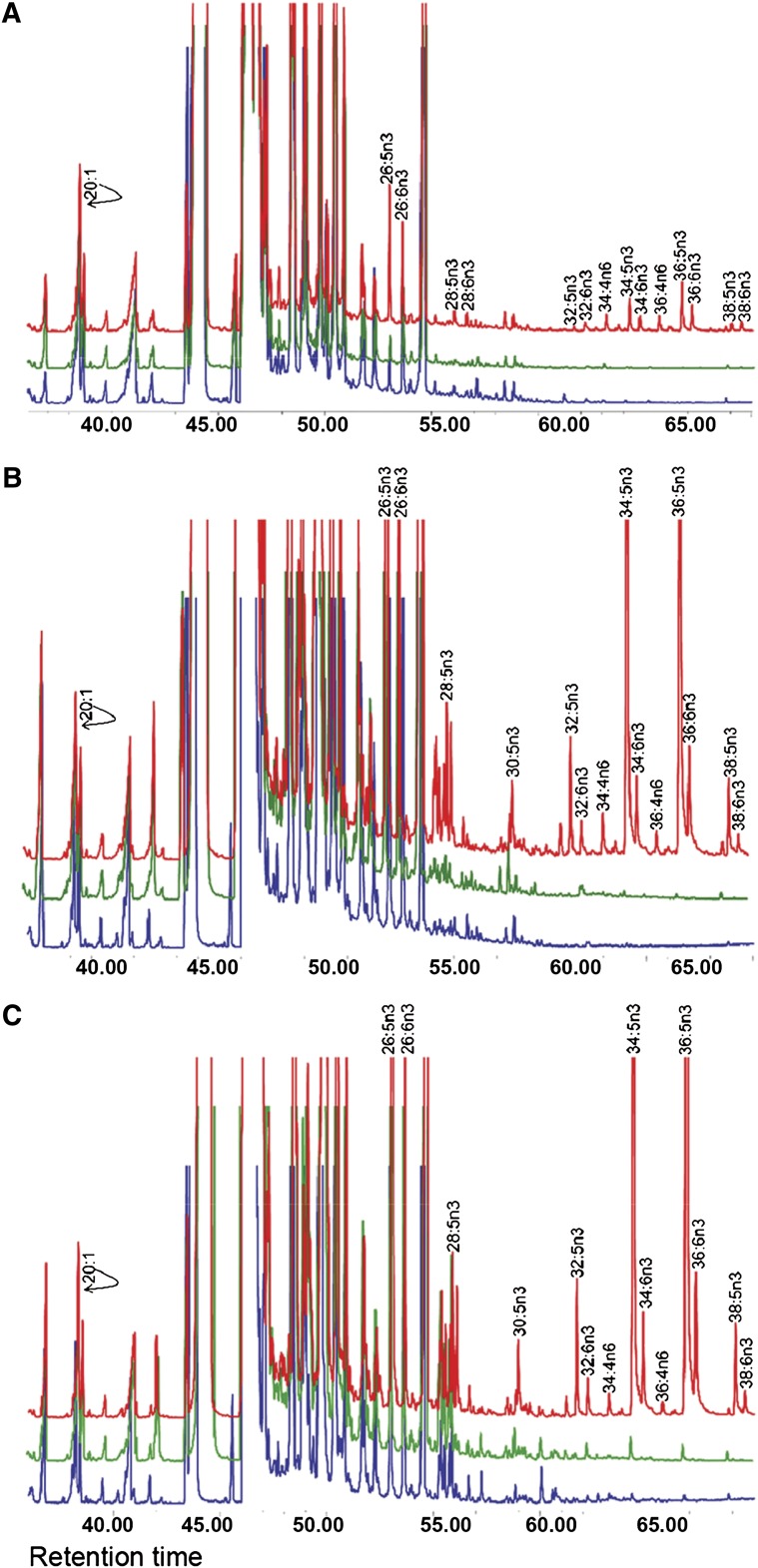
Fig. 5.
Biosynthesis of VLC-PUFA in cardiomyocytes that express Elovl4 transgene. GC-MS was used to identify the VLC-PUFA derived from cardiomyocytes treated with either 20:5n3 or 22:5n3 for 72 h after transduction with recombinant Elovl4 or GFP viruses for 24 h. The PUFA response values were obtained by using the m/z ratios 79.1, 108.1, and 150.1 in SIM mode and abundances were compared by normalizing the chromatograms to the response of 20:1. A: Rat cardiomyocytes expressing mouse Elovl4 (red) minigene or GFP (green) and nontransduced cells (blue) were cultured without precursors for 72 h. All cells, irrespective of ELOVL4 expression, synthesized C22-C26 PUFA. ELOVL4 expression in the absence of precursors resulted in the elongation of an endogenous precursor to C28-C38 VLC-PUFA. B: Cardiomyocytes in A above cultured with 20:5n3 synthesized C24-C26 in all treatment groups. Significant biosynthesis of C28–C38 n3 VLC-PUFA occurred in Elovl4-transduced cells (red), but not in GFP (green) and nontransduced cells (blue), with accumulation of 34:5n3 and 36:5n3. C: Cardiomyocytes in A above cultured with 22:5n3 synthesized C24-C26 in all treatment groups. They also synthesized the same n3 VLC-PUFA as found when 20:5n3 was used as the substrate. Note that each chromatogram was normalized to endogenous 20:1, which did not change among the sample groups. Reprinted from Agbaga et al. (39) with permission from publishers.