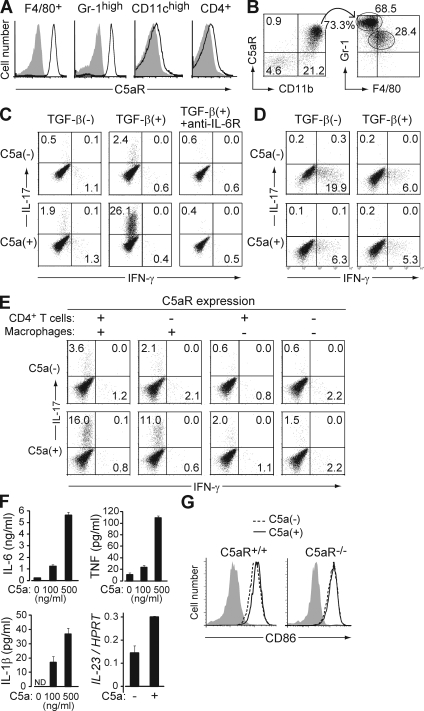
Figure 3.
C5a acts on tissue-resident macrophages to facilitate Th17 cell differentiation. (A) F4/80+ cells in the peritoneal cavity, and Gr-1high, CD11chigh, and CD4+ cells in the spleen of nontreated SKG mice were stained for C5aR (continuous line) or isotype control (shading). (B) Cells infiltrating in the arthritic joint of mannan-treated SKG mice were stained for C5aR, CD11b, Gr-1, and F4/80. C5aR+ CD11b+ cells are shown for the expression of Gr-1 and F4/80. (C) BALB/c CD4+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and cultured with resident peritoneal macrophages in the presence or absence of TGF-β, recombinant C5a, or anti–IL-6R, and stained for intracellular cytokines on day 3. (D) Intracellular cytokine staining of BALB/c CD4+ T cells cultured with splenic DCs in the presence or absence of TGF-β and C5a. (E) Intracellular cytokine staining of CD4+ T cells after criss-cross co-culture with C5aR+/+ or C5aR−/− CD4+ T cells and C5aR+/+ or C5aR−/− macrophages in the presence of TGF-β. (F) ELISA assessment (triplicates) for IL-6, TNF, and IL-1β produced by macrophages, or quantitative RT-PCR for their IL-23 mRNA expression, when macrophages were stimulated overnight by C5a at the indicated doses. Error bars are means ± SD. (G) CD86 expression on C5aR+/+ or C5aR−/− macrophages cultured with or without C5a for 4 h. Shading indicates isotype control. Results in A–G represent three independent experiments. Numbers in B–E indicate percentages.