Fig. 5.
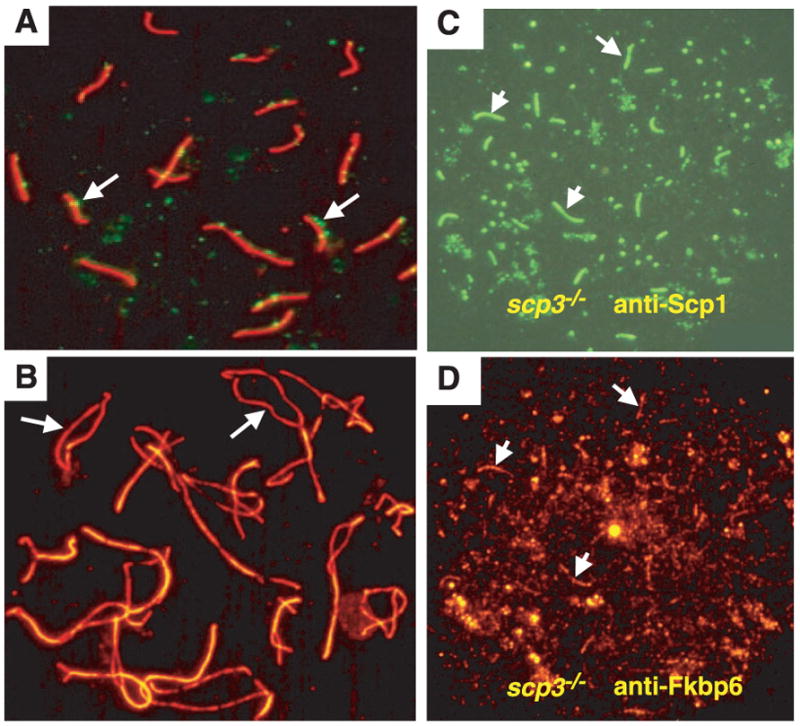
Fkbp6 colocalizes with Scp1 in synapsed chromosomes of Scp3−/− spermatocytes. (A) Normal SC formation in pachytene oocytes stained with Scp3-rhodamine and FITC-labeled antibodies to Rad51 and Dmc1. Rad51 and Dmc1 foci (arrows) define regions of double-strand breaks. (B) Normal chromosome separation (arrows) in diplotene oocytes stained with Scp3-rhodamine, in a 1-day-old Fkbp6−/− female. (C and D) Expression of Fkbp6 and Scp1 in synapsed regions of Scp3−/− zygotene spermatocytes. (C) Short stretches of FITC-labeled Scp1 mark synapsis between the chromosome cores. (D) Fkbp6 (rhodamine) expression at the residual synapsed regions of Scp3−/− zygotene spermatocytes. Arrows in (C) and (D) show Scp1 and Fkbp6 colocalization.
