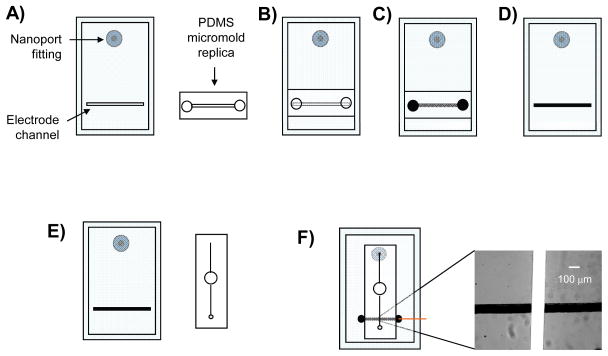
Figure 1.
Steps involved in fabrication of PDMS-embedded carbon electrodes and assembly of the reservoir device (not to scale). A) PDMS layer where the carbon microelectrode will be embedded is reversibly sealed to a glass plate containing a Nanoport fitting. Also shown is the replica top micromold; B) The replica micromold is aligned and reversibly sealed over the electrode channel in the PDMS layer creating an encapsulated void; C) A vacuum is applied to one end of the top micromold while carbon ink is applied to the opposite end and pulled through the micromolds; D) After a heating step, the top micromold is removed leaving a cured carbon microelectrode structure embedded in the PDMS layer; E) The fluidic layer containing the 1/8″ diameter reservoir and the separate PDMS layer containing the carbon ink electrode are shown. F) The two PDMS layers are aligned and reversibly sealed together crating a fully assembled reservoir device. The inset shows fluorescein flowing through the fluidic channel and over the carbon ink microelectrode.