Figure 1.
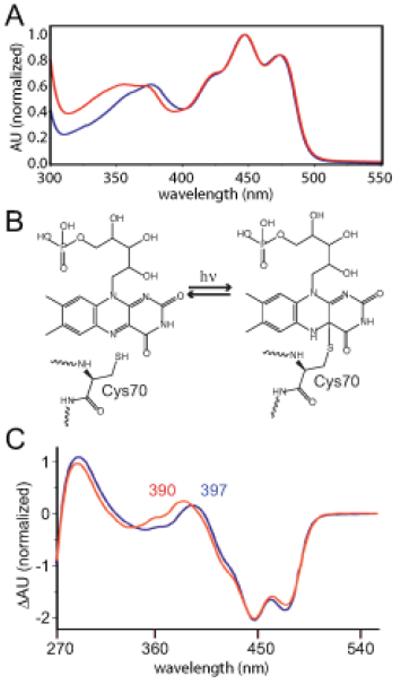
(A) Absorption spectra of C. crescentus LovK (red) and A. sativa phot1-LOV2 (blue). (B) Cartoon illustrating light-dependent adduct formation between LovK residue C70 and C(4a) of the FMN isoalloxazine moiety. (C) Light minus dark difference absorption spectra of C. crescentus LovK (red) and A. sativa phot1-LOV2 (blue). Absorption maxima for the adduct species in LovK (390 nm) and phot1-LOV2 (397 nm) are labelled
