Fig. 9.
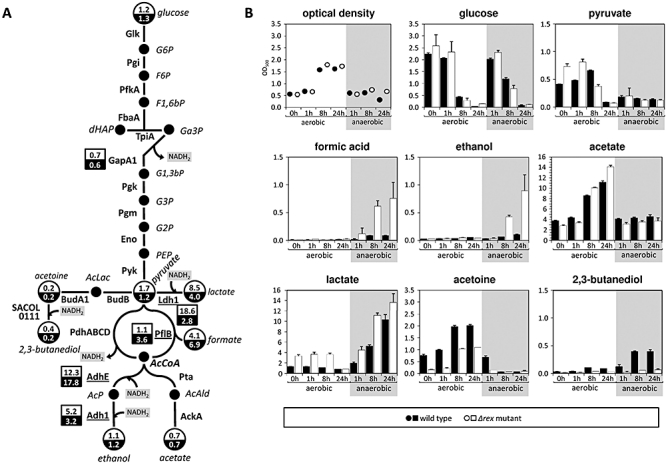
Impact of Rex on selected metabolic pathways. A. Selected proteomic and metabolomic data of the glycolysis and fermentation pathways. Protein synthesis rates (rex mutant/wild-type) of selected enzymes are shown in squares and ratios of selected metabolites (rex mutant/wild-type) are shown in circles for aerobic (white) and anaerobic (black) conditions. Proteins whose genes are directly Rex-regulated are underlined. Cells were grown in synthetic medium without MOPS buffer to an optical density of 0.5 and shifted to anaerobic conditions. Cytoplasmic proteins of the wild-type and rex mutant were labelled with l-[35S]-methionine before and 60 min after a shift to anaerobic conditions and separated on 2D gels. The resulting 2D gel images were analysed using Delta2D software (DECODON, Greifswald). For metabolite analyses, samples were taken from the aerobically grown culture and from the anaerobically grown culture immediately before (only aerobic culture) and 1, 8 and 24 h after shifting to anaerobic conditions. Cells were separated from the supernatant by filtration and the supernatants obtained were used for further analyses. B. Extracellular metabolite analyses by 1H-NMR. Glucose, pyruvate, formic acid, ethanol, acetate, lactate, acetoine and 2,3-butanediol were detected and quantified by 1H-NMR. The graphs show the increase of the concentration in mM.
