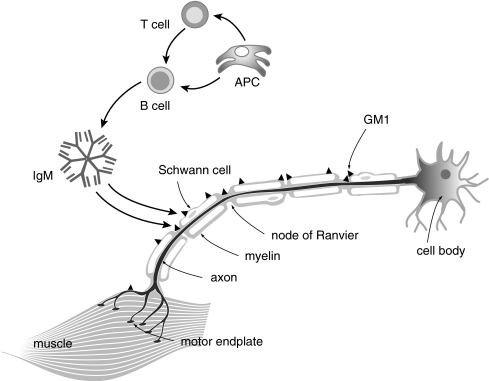
Fig. 1.
Schematic depiction of assumed key players in MMN pathogenesis. Anti-GM1 IgM and possibly other antibodies are produced by B cells that may be specifically activated by antigen presenting cells (APC), or through “bystander” effects. There are no indications that T cells are involved. These IgM antibodies may bind to GM1 in nerves if the blood-nerve barrier is leaky, and may locally activate complement. The deposition of complement disrupts the architectural integrity of the nodes of Ranvier and paranodal regions, causing local disruption of Na+ channel clusters. This may ultimately contribute to axonal depolarization or hyperpolarization and conduction block. IVIG might interfere with B-cell antibody production through binding to the B-cell receptor or inducing inhibitory receptors, with anti-GM1 antibodies through anti-idiotypic effects, or it might attenuate complement deposition