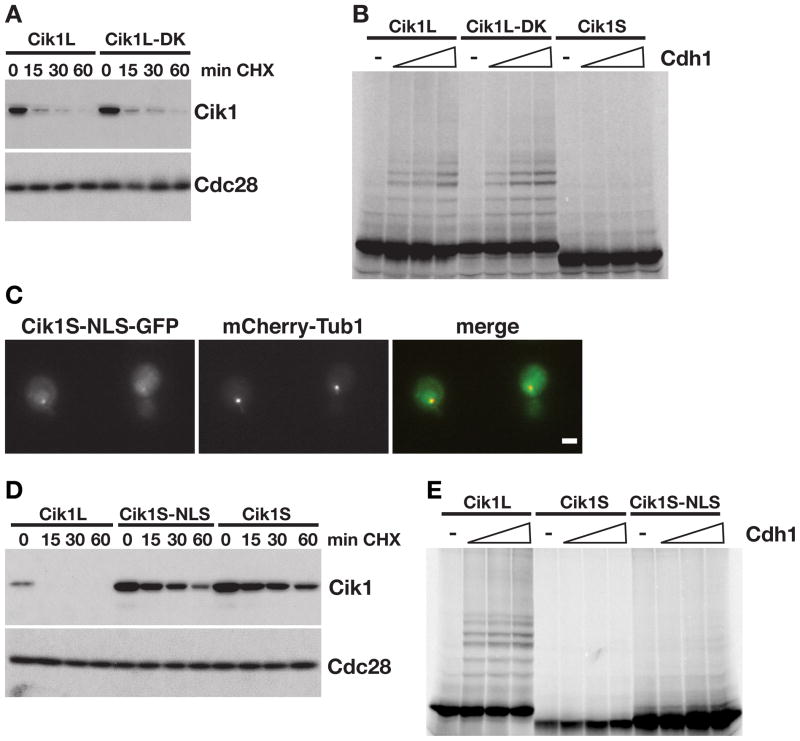
Figure 4. Cik1L is a direct target of APC/CCdh1.
(A) Cycloheximide-chase assay showing levels of Cik1 in Cik1L (TEFp-CIK1) and Cik1L-DK (TEFp-CIK1-DK) cells after addition of cycloheximide for the indicated times (min CHX). Cell cycle profiles are shown in Figure S4A. (B) Cik1L, Cik1L-DK and Cik1S were translated in vitro and labeled with 35S-methionine. Equivalent amounts were incubated with purified E1, E2, ATP, ubiquitin, and APC/C in the absence (−) or presence of Cdh1 (100, 200, or 400nM). Reactions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and visualized with a phosphorimager, quantitation is shown in Figure S4B. (C) Cik1S-NLS-GFP and mCherry-Tub1 expression. GFP, mCherry and merged images are shown. Scale bar represents 2μm. (D) Cycloheximide-chase assay showing levels of Cik1 in Cik1L (TEFp-CIK1), Cik1S-NLS (TEFp-ΔATG-CIK1-NLS), and Cik1S (TEFp-ΔATG-CIK1) cells after α factor arrest followed by the addition of cycloheximide (min CHX). Cell cycle profiles are shown in Figure S4C. (E) In vitro ubiquitination of Cik1L, Cik1S and Cik1S-NLS by the APC/C as described in (B), except that 50, 150, or 300nM Cdh1 was added. Quantitation is shown in Figure S4D.