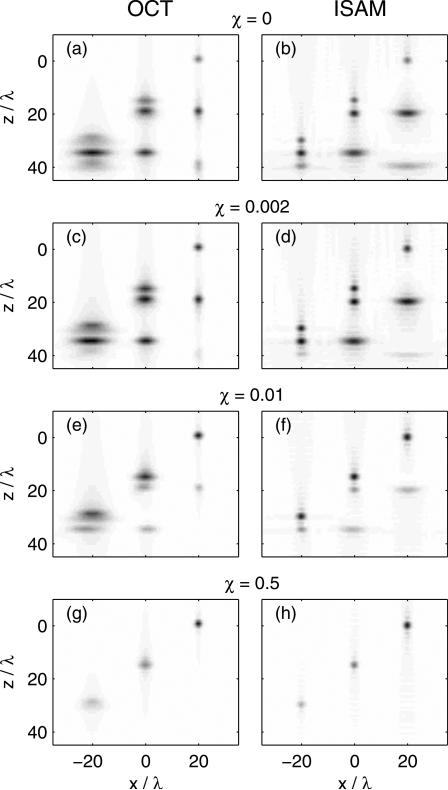
Fig. 4.
(a), (c), (e), (g) OCT and (b), (d), (f), (h) ISAM images of an object consisting of three point scatterers at (20,0,0)λ, (0,0,15)λ, and (–20,0,30)λ. The source spatial coherence is varied as described by the parameter χ, the numerical aperture of the objective is 0.2 and the focal plane is at z=0. The coherence lengths are (a), (b) ∞ (χ=0), (c), (d) 25λ (χ=0.002), (e), (f) 11λ (χ=0.01), and (g), (h) 1.1λ (χ=0.5). The images are formed from data consisting of first- and second-order scattering effects. A projection over the y axis of the three-dimensional image magnitudes is taken to produce the two-dimensional images displayed.