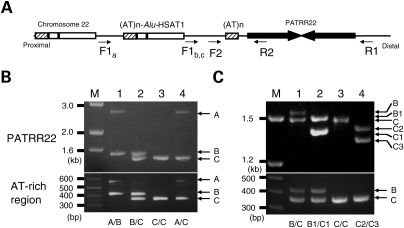
Figure 2.
Screening and genotyping of rare short PATRR22 variants. (A) Genomic structure of the PATRR22 region. LCR-specific primers are designed to amplify the PATRR22 (arrows). Proximal region represents the ‘AT-rich region-HSAT1-Alu’ cassette repeated three or four times (6,29). Sites for the forward primer (F) carry sequence variations among the AT-rich region polymorphic alleles. In the B and C alleles, the PCR product originates from the closest F site, whereas it can anneal with the second closest site in the A allele. (B) LCR-specific PCR for amplifying the PATRR22. Upper panel represents the LCR-specific PCR for the PATRR22, whereas the lower panel indicates the genotyping of the AT-rich region flanking the PATRR22. Genotypes of the AT-rich region are given at the bottom. The PATRR22-specific PCR product from the A allele is much longer than the others for the reason described above. M, size markers. (C) Rare variants. Lane 1, standard B/C heterozygote; lane 2, compound heterozygote for B/C rare variants; lane 3, C/C homozygote; lane 4, compound heterozygote for C rare variants.