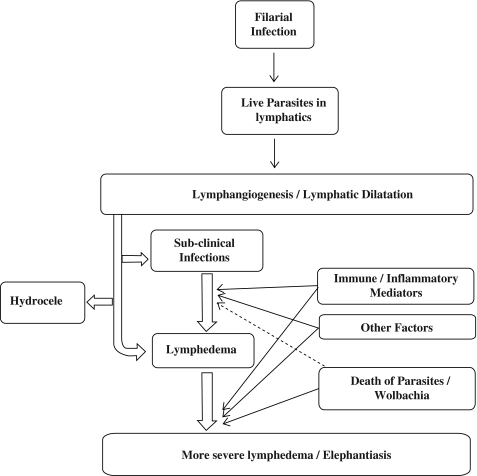
FIG. 2.
Establishment of filarial infection results in live adult parasites lodged in the lymphatics that result in lymphatic abnormalities. The transition from the asymptomatic microfilaremic state to chronic lymphatic obstructions varies widely in infected individuals. Lymphatic dilatation is, however, a prominent feature irrespective of the clinical manifestations. The interplay between the immune/inflammatory mediators, slow attrition of the parasites coupled with other factors affect the development of lymphedema. The death of the parasites stimulates strong inflammatory responses to the parasite and to the products of their Wolbachia endosymbionts, leading to tissue fibrosis. Secondary microbial infections further aggravate the pathology.