Figure 2. Schematic illustration of the four sufficient conditions for sign determinedness, C1–C4.
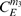 is the concentration control coefficient of m3 with respect to the reaction catalyzed by E.
is the concentration control coefficient of m3 with respect to the reaction catalyzed by E. |
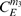 is the concentration control coefficient of m3 with respect to the reaction catalyzed by E.
is the concentration control coefficient of m3 with respect to the reaction catalyzed by E. |