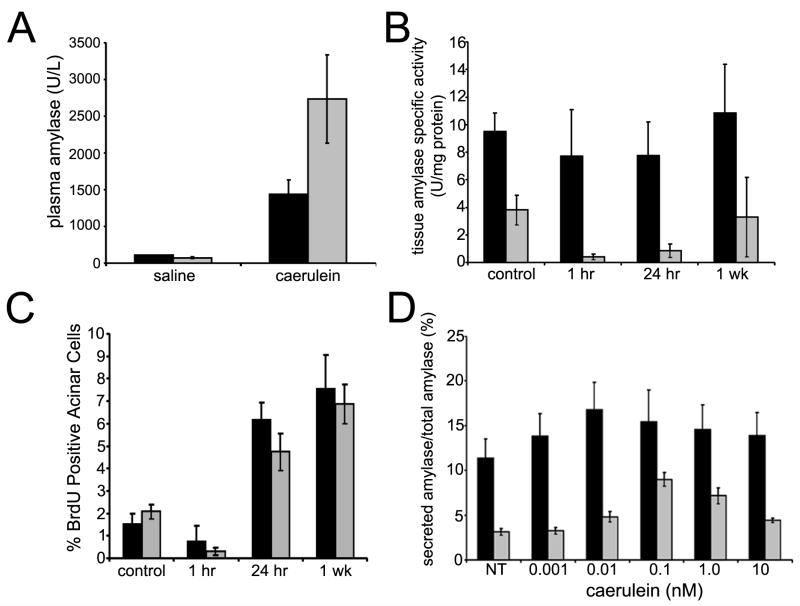
Figure 5. Caerulein response in β1-Itgflox/flox;Ptf1a-Cre mice.
(A) Plasma amylase levels from caerulein-treated mice 1 hour after recovery. Normalized to saline-injected controls, the relative increase after caerulein treatment in β1-Itg flox/flox;Ptf1a-Cre mice (grey bars) was >2 fold greater than wild type (black bars). Averages of 3 or more mice/group; error bars ± SEM. (B) Wild type pancreatic lysates did not show significant changes in tissue amylase after caerulein injection. β1-Itgflox/flox;Ptf1a-Cre (grey bars) saline-injected controls had significantly less tissue amylase activity than wild type. Normalized to saline-injected controls, β1-Itgflox/flox;Ptf1a-Cre pancreatic lysates showed a decrease (P<0.05) at 1 and 24 hours post-treatment. (C) Acinar cell proliferation was measured by immunohistochemistry for BrdU incorporation. Relative incorporation was similar at 1 hr, 24 hrs and 1 week after caerulein treatment in wild type and β1-Itg flox/flox;Ptf1a-Cre mice. Each bar represents blind counts of BrdU positive nuclei divided by total acinar cells from of 3 randomly selected 40X fields from each of 5 slides/mouse, 3 mice/time point and treatment condition. Error bars ± SEM. (D) Primary acinar cell explants were treated with caerulein at various concentrations. Conditioned media and lysates were collected after 30 minutes and amylase activity determined. Media amylase relative to total amylase is depicted. Maximal amylase levels were found at 10 pM (wild type) and 100 pM (β1-null) caerulein. (Averages from triplicate assays for 3 or more mice; error bars ± SEM).