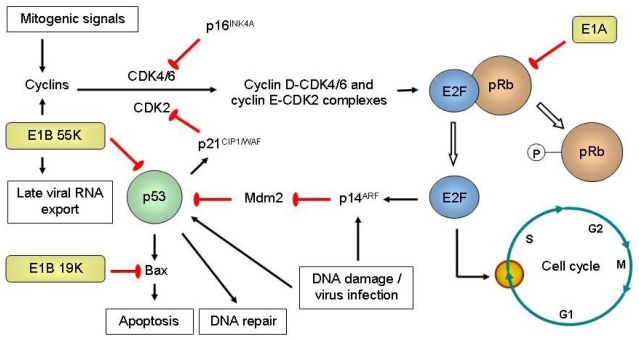
Figure 2.
Engineered replication selectivity of oncolytic adenoviruses (Ads) by deletion of the E1A, E1B 19K or E1B 55K gene. Retinoblastoma protein (pRb) is normally hypophosphorylated and binds to transcription factors of the E2F family to regulate the G1-to-S checkpoint of the cell cycle. Upon stimulation by mitogenic signals, upregulation of cyclins enables cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) to phosphorylate pRb, releasing E2F that leads to the expression proteins needed for DNA synthesis and thus cell cycle progression. E2F upregulates p14ARF, which inhibits Mdm2. Mdm2 normally results in p53 degradation. p53 is a transcription factor that is upregulated and activated by stress signals such as virus infection or DNA damage. It results in the expression of proteins that induce apoptosis (Bax), cell cycle arrest (p21CIP1/WAF via its inhibition of CDK2) or DNA repair. p16INK4A is a tumor suppressor that inactivates CDK4/6. The adenoviral E1A proteins bind to pRb to release E2F, so that viral DNA could be replicated. E1A also promotes the acetylation of pRb by p300/CBP, causing pRb to associate with Mdm2 to inhibit p53. Because cancer cells are often in the S phase, E1A CR2-deleted Ad5 mutant (dl922-947) could selectively replicate in and destroy replicating cancer cells but not normal resting cells [29]. E1B 19K binds to and inhibits Bax. The tumor selectivity of E1B 19K-deleted Ad2 (dl250) is due to multiple defects in the apoptotic pathways, where survival of the virus in normal cells would be limited owing to rapid apoptosis induction in the presence of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) [30]. E1B 55K interacts with the adenovirus E4 open reading frame 6 (E4orf6) protein to form an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that targets p53 for degradation. It also induces the expression of cyclin E as well as simultaneously inhibits cellular mRNA export and promotes the export of late viral mRNAs. E1B 55K-deleted Ad could replicate in tumor selectively because of non-functioning p53 [31], cyclin E overexpression [32], and E1B 55K-independent late viral RNA export in cancer but not normal cells [33].