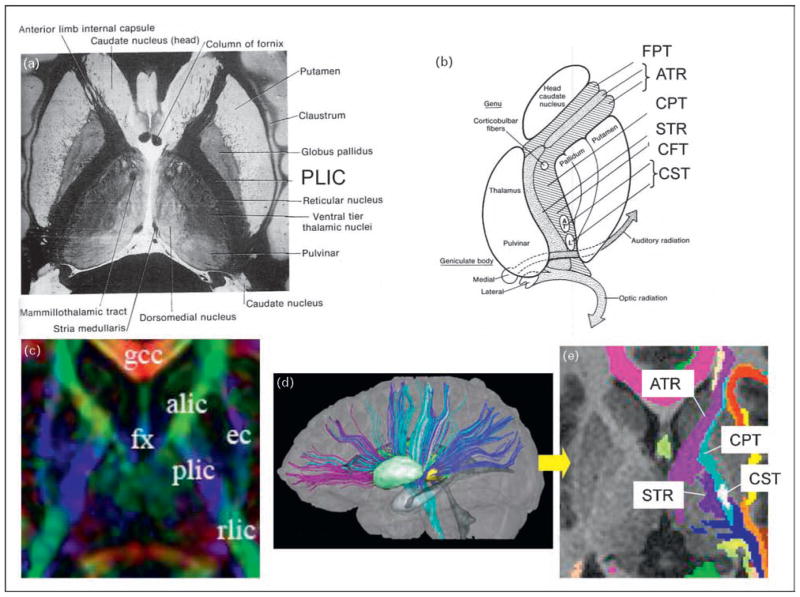
Figure 4. Comparison between histology-based and diffusion tensor imaging-based white matter atlases.
(a) Classic ‘point and annotate’ (location-based) atlas of a human brain using a histology section. (b) Schematic diagram of white matter tract structures inside the internal capsule (connection-based atlas). Inside the posterior limb of the internal capsule (PLIC), there are several axonal tracts with different destinations, which include the superior thalamic radiation (STR), the corticopontine tract (CPT), the corticospinal tract (CST), and other corticofugal tracts (CFT; a generic description of all axons descending from the cortex, including the CPT and the CST). (c) A diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) version of the location-based point and annotate atlas similar to that in panel (a). In this image, the color represents pixel-by-pixel information about the fiber orientation: red, right–left; green, anterior–posterior; and blue, superior–inferior. (d) Three-dimensional reconstruction results from the white matter tracts penetrating the PLIC. (e) A connection-based atlas similar to that in panel (b). The color-coding represents the location at the given slice level of the anterior thalamic radiation (ATR), the CPT, the CST, and the STR, reconstructed in (d). The figures in (a) and (b) are reproduced with permission from [19].