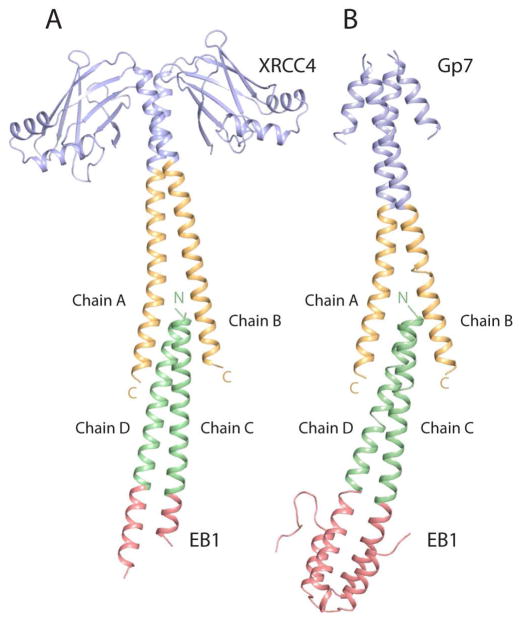
Figure 3.
Ribbon representation of the two avian smooth muscle tropomyosin overlap structures. A) The structure of the XRCC4-TmC:TmN-EB1 complex. This was obtained by fusing residues Glu2-Ala135 of XRCC4 (blue) to the C-terminal residues Lys248-Met284 of tropomyosin (orange) and fusing the N-terminal residues Met1-Lys29 of tropomyosin (green) to residues Asp215-Asp257 of the C-terminal helix bundle of EB1 (red). B) The structure of the Gp7-TmC:TmN-EB1 complex. The Gp7-TmC construct was made by fusing residues Pro2-Asp45 of Gp7 (blue) to the C-terminal residues Leu256-Met284 of tropomyosin (orange). The chain labels are included in this figure. Chains A and B belong to the C-terminal fragment of tropomyosin, whereas chains C and D belong to the N-terminal fragment. Figures 3, 4, 6, and 8 were prepared with Pymol (DeLano, 2002).